Table of Contents
1. What is Grinding?
Grinding is a mechanical processing method that uses grinding wheels on grinding machines to perform finishing and superfinishing operations on workpieces. Workpieces processed through grinding can achieve high precision and low surface roughness values. Compared to other cutting methods, grinding not only enables the processing of high-hardness materials such as hardened steel and cemented carbide but also allows for high-quality machining of complex-shaped surfaces. As a result, it is widely applied in fields such as precision machinery, mold manufacturing, and the automotive industry.

2. Common Types of Grinding Machines
Grinding machines can be classified according to their purpose and structure into instrument grinding machines, external cylindrical grinding machines, internal grinding machines, tool grinding machines, surface grinding machines, and spline grinding machines. In addition, there are thread grinding machines, gear grinding machines, and other special-purpose grinding machines.
3. Composition and Function of a Grinding Machine
1. Bed: Connects and supports all components of the grinding machine. It houses the hydraulic transmission system and is typically constructed as a box-type structure to enhance rigidity.
2. Workbench: Drives the workpiece in reciprocating motion, controlled by a manual or hydraulic transmission system. The workbench is divided into an upper workbench and a lower workbench.
3. Grinding Wheel Spindle: Supports the grinding wheel and performs lateral feed motion. The motor on the grinding wheel spindle drives the grinding wheel to rotate at high speed and perform lateral feed, controlled by a manual or hydraulic transmission system.
4. Column: Mounts the grinding wheel spindle and drives it for vertical feed motion.
5. Hydraulic transmission system: The primary transmission mechanism of the grinding machine. Hydraulic transmission features smooth operation, simple and convenient control, it can achieve stepless speed variation over a wide range, it has self-lubricating properties. However, the transmission ratio is not precise.
6. Cooling and lubrication system.

4. Characteristics of Grinding Processing
1. Minimal machining allowance and high machining accuracy. General grinding can achieve accuracy levels of IT5 to IT7, with surface roughness as low as Ra0.1 μm to Ra0.8 μm.
2. Grinding has a wide range of applications, capable of processing inner and outer cylindrical surfaces, conical surfaces, flat surfaces, gear surfaces, and helical surfaces. It can also be used to grind ordinary ductile materials, castings, and other brittle materials, as well as hardened steel, cemented carbide, and gemstones—materials that are difficult to machine due to their high hardness.
3. High grinding speed, high energy consumption, low cutting efficiency, high grinding temperature, and the workpiece surface is prone to defects such as burning and residual stress.
4. The grinding wheel has a certain degree of self-sharpening. This allows new edges to form, maintaining the sharpness of the grinding wheel.
5. Motion Forms in Grinding Processing
Taking an external cylindrical grinder as an example
(1) The primary motion is the high-speed rotation of the grinding wheel.
(2) Circumferential feed motion: The workpiece rotates around its axis.
(3) Longitudinal feed motion: The workpiece moves back and forth with the worktable.
(4) Transverse feed motion: The grinding wheel cuts into the workpiece along its axis.
Taking a surface grinder as an example
(1) The main motion is the high-speed rotation of the grinding wheel.
(2) Longitudinal feed motion: The workpiece moves back and forth with the worktable.
(3) Transverse feed motion: The grinding wheel moves back and forth along its axis.
(4) Vertical feed motion: The grinding wheel and grinding wheel holder move along the column guideways.
6. Characteristics of Abrasive Tools and Their Selection
1. Types of Abrasive Tools
Conventional Abrasive Tools: Abrasive tools made from corundum, silicon carbide, and boron carbide abrasives. Superhard Abrasive Tools: Abrasive tools made from high-hardness abrasives such as diamond and cubic boron nitride. Bonded Abrasive Tools: Grinding wheels, oilstones, grinding blocks, grinding heads, and polishing blocks.
Coated abrasives: sandpaper, sandcloth, sandbelts.
Grinding paste: A polishing agent composed of abrasive materials and grinding and polishing liquid.
2. Characteristics and Selection of Grinding Wheels
Grinding wheels consist of abrasive materials, bonding agents, and pores (three elements). The characteristics of grinding wheels depend on the abrasive materials, particle size, bonding agents, hardness, structure, and shape and size. The characteristics and applicable ranges of grinding wheels are shown in the table Characteristics and Applicable Ranges of Grinding Wheels.
| Types | Code | Abrasive name | Color, hardness, rigidity | Scope of Application |
| Oxides | GZ | Brown corundum | Brownish-gray, high hardness, high toughness | Carbon steel, alloy steel |
| GB | White corundum | White, hardness > GZ, low toughness | Quenched steel, high-speed steel | |
| Silicon carbide | TH | Black silicon carbide | Black, hardness > GB, low toughness, sharp | Brass, non-metals, cast iron, etc. |
| TL | Green silicon carbide | Green, hardness > TH, brittle | Hard alloys, ceramics, etc. |
7. Cooling System
1. The Role of Coolant
High temperatures are generated in the grinding zone, sometimes exceeding 1000°C. Under such conditions, the workpiece may suffer from burning, deformation, or cracking. Therefore, it is essential to select an appropriate coolant that serves the following functions.
(1) Cooling the workpiece: Reducing the temperature in the grinding zone.
(2) Cleaning function: Removing grinding debris and abrasive particles to prevent scratching the workpiece.
(3) Lubrication function: Reducing friction between the workpiece surface and abrasive particles.
(4) Rust prevention: Prevent rusting of the workpiece and machine tool.
2. Types of Coolants
Common coolants include water-based, oil-based, and solid types. In actual production, non-toxic and environmentally friendly coolants should be selected based on the processing requirements of different parts.
8. Grinding Methods
The most common grinding methods are mainly external cylindrical grinding and surface grinding, as shown in the figure.
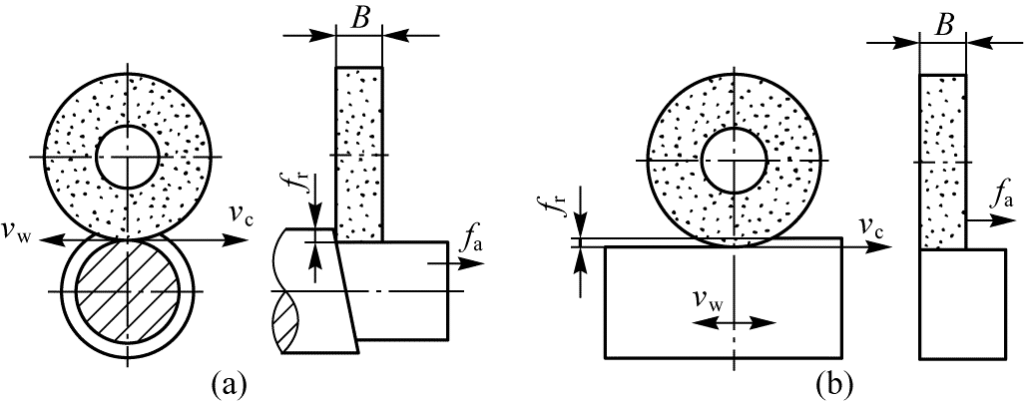
1. There are two main grinding methods for external cylindrical grinders:
Longitudinal grinding method: This method produces high-quality results but has lower efficiency. It is suitable for grinding workpieces longer than the width of the grinding wheel and for finishing operations.
Transverse grinding method: This method has high grinding efficiency but slightly lower grinding quality than the longitudinal grinding method. It is suitable for rough grinding and for grinding workpieces shorter than the width of the grinding wheel. Combining both methods is referred to as the comprehensive grinding method.
2. There are two main grinding methods for surface grinders:
Circumferential grinding method — uses the circumferential surface of the grinding wheel to grind the workpiece, with low grinding efficiency but good grinding quality.
End grinding method — uses the end face of the grinding wheel to grind the workpiece, with high grinding efficiency but slightly lower grinding quality than the circumferential grinding method, suitable for mass production, and primarily applicable to circular surface grinders.
3. Precautions for grinding wheel installation
(1) The grinding wheel is a high-speed rotating tool. It must be inspected for cracks, breaks, etc., and must be securely clamped and installed correctly.
(2) For grinding wheels with a large diameter (grinding wheel diameter greater than 125 mm), a balancing test must be performed.
(3) After a period of use, the working surface of the grinding wheel must be dressed using diamond tools.
9. Conclusion
In actual production, selecting the appropriate grinding machine type, grinding tool material, coolant, and grinding method, and strictly adhering to installation and operating procedures, not only extends the service life of equipment and grinding tools but also ensures the stability and reliability of workpiece processing quality. As a professional precision machining service provider, we not only possess advanced CNC grinding machine equipment but also have an experienced machining team, capable of providing customized grinding services including external cylindrical grinding, internal cylindrical grinding, and planar grinding. Whether it is single-piece prototyping or mass production, we can ensure that dimensional accuracy and surface quality meet strict standards, providing reliable support for your project delivery.