CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. It refers to the automated, computer-controlled operation of machine tools (such as mills, lathes, routers, or drills) to shape parts by cutting away material from a solid block. In contrast to manual machining, CNC systems use digital instructions (often in the form of G-code) to control every movement of cutting tools, enabling high precision and repeatability. CNC parts can range from small electronic components to large aircraft structures, reflecting the versatility of the process.
In this guide, we explain what CNC machining is, how it works, its history, the materials used, the key steps in the process, as well as its advantages, limitations, and how it compares to 3D printing. We also offer tips on selecting a machining supplier and discuss the current demand for CNC services.
Table of Contents

What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a way of processing parts. It processes raw materials to make them meet the final requirements and have relatively high precision and quality. CNC machining involves many technologies and processes and can be processed by almost all raw materials, such as metals, plastics, powder metallurgy, etc.
The process of cnc machining includes design, CAD analysis, transmission, programming, process analysis, equipment reorganization, processing, inspection and maintenance. Among them, the design and process analysis are very important. The accuracy of these two links determines the quality of machined parts. Designers need to make accurate drawings of parts, including specific dimensions and requirements. Process analysis requires analyzing the processing plan and making a reasonable process plan.
The key part of cnc machining is the machine tool, which is a machine used to process raw materials. Machine tools are used for cutting, drilling, milling, turning, high-speed milling, CNC machining and other aspects. The accuracy and quality of machine tools are the key to machining. The manufacture of machine tools requires strict control of all aspects of materials, design and manufacturing to ensure the quality of machine tools.
CNC machining can be used for various materials, and metal is the most common material for cnc machining. Metals have the advantages of high strength, good electrical conductivity and excellent corrosion resistance. Common traditional materials include copper, aluminum, steel, etc., and there are also new high-strength metals such as titanium alloys. In addition, machining can also be applied to raw materials such as plastics and powder metallurgy to make them into the required final parts.
There are many things to pay attention to during machining, such as operating specifications, safety, quality control, etc. CNC machining, as a high-precision processing method, requires attention to the quality control of machine tools, tools, raw materials and processing. During the processing, the equipment and workplace should be kept clean, and the residues in other places of the working raw materials should be cleaned up in time. When performing cnc machining operations, labor protection supplies such as safety helmets, protective gloves, and goggles must be used to ensure personal safety at work.
In short, cnc machining is an indispensable technology in the manufacturing industry and has become an important part of modern manufacturing. The development of machining technology plays a vital role in the transition from manual manufacturing to modern machine automation manufacturing. Through the development of science and technology, machining technology will continue to develop and bring more outstanding achievements to the manufacturing industry.
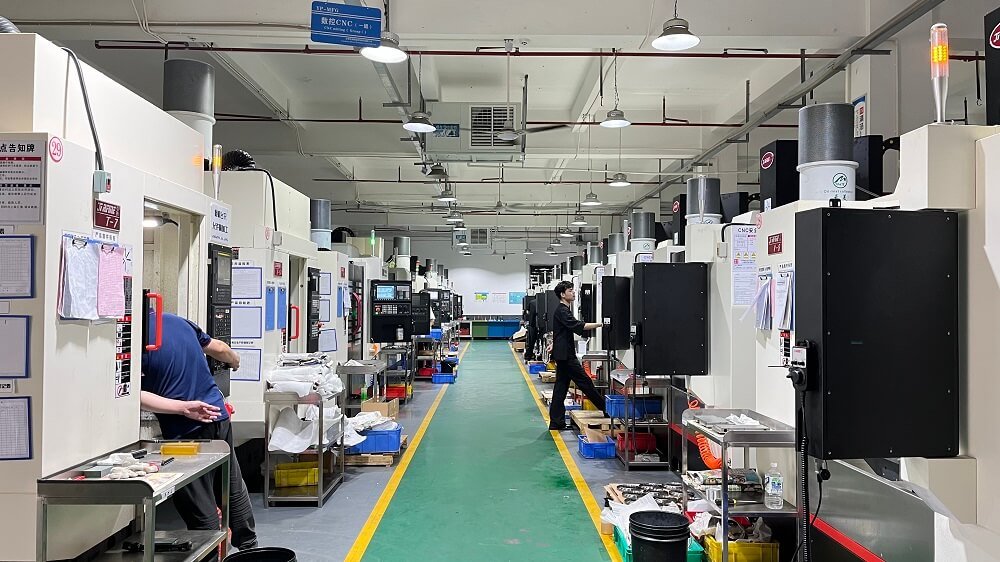

How Does CNC Machining Work?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining works by automating the movement and operation of cutting tools through computer programming. Unlike manual machining, where an operator must guide each cut by hand, CNC machining uses pre-programmed instructions to precisely control how tools move and interact with the raw material. It ensures high accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency — even for complex shapes.
CNC Machining Process
Machining is the process of machining through machine tools and other machine equipment to achieve the requirements of part accuracy and quality. The process of machining usually includes design, CAD analysis, transmission, programming, process analysis, equipment preparation, processing, inspection and maintenance. Now, let’s take a look at the specific process of machining.
1. Design
Design is the first link in machining. Designers need to make drawings of parts, including detailed dimensions and requirements. Designers also need to analyze factors such as the material properties and use environment of the required parts to ensure that the design plan meets the actual requirements.
2. CAD analysis
CAD analysis is a link in computer-aided design and analysis, and CAD software is required for design analysis. In this link, designers can use CAD software to perform 3D modeling, process analysis and other processes to enhance the design reliability of parts, improve production efficiency, and ultimately produce high-standard quality products.
3. Programming
According to the design plan, programmers can write machining programs and integrate them into the control system of mechanical equipment. The machining program includes tool paths and cutting parameters, and each parameter should be reasonably set according to the actual situation.
4. Process analysis
In the process analysis stage, it is necessary to analyze the processing plan and formulate the processing flow, standards and processing technology to ensure that the parts restore the design and meet the quality and precision requirements.
5. Equipment preparation
Equipment preparation is an important step in machining. It is necessary to inspect the equipment, replace the equipment tools, and repair the equipment to ensure that the equipment can start normal processing. During the equipment preparation process, it is also necessary to predict the needs of materials and components to ensure that the equipment can work smoothly.
6. Processing
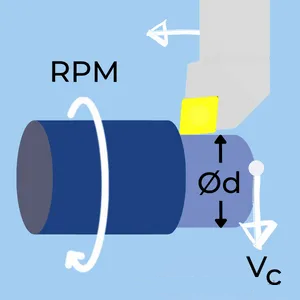
Processing is the core step of machining. It is to cut, drill, mill, turn and other processing of different materials to produce parts that meet actual requirements. During the processing process, it is necessary to reasonably control the cutting speed, tool selection, processing method, etc., to ensure the processing quality of parts.
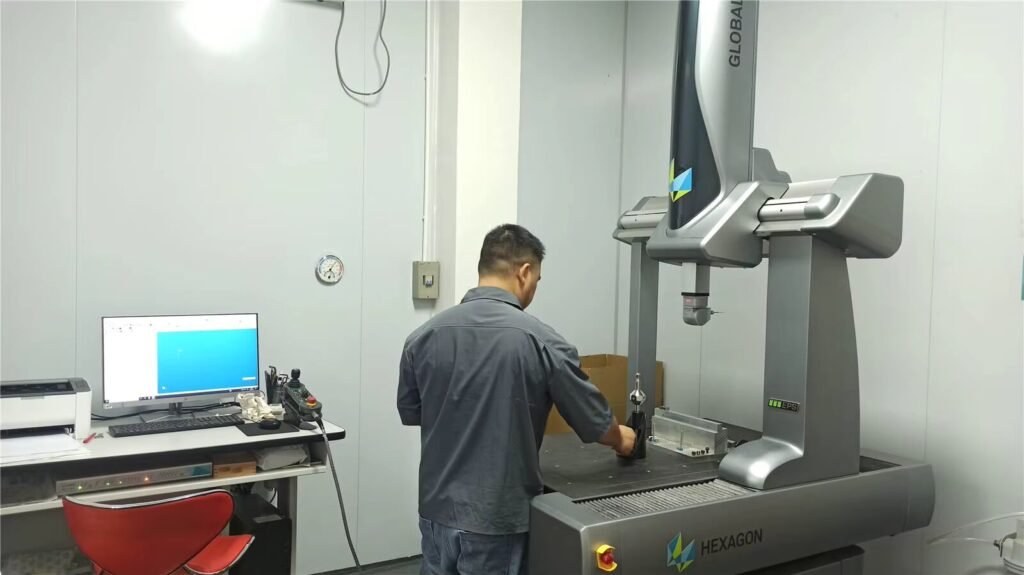
7. Inspection
After the machining is completed, the parts need to be inspected to ensure that their quality and precision meet the design requirements. During the inspection process, relevant testing equipment and instruments, such as calipers, angle rulers, microscopes, high-precision measuring instruments, etc., need to be used to ensure that the quality of parts meets the requirements.

8. Maintenance
Machining equipment requires daily maintenance to ensure stable operation and long life of the equipment. During the maintenance process, the gears, belts, oil, etc., of the equipment need to be maintained, and the various components on the machine tool need to be cleaned and inspected to ensure the long-term operation of the equipment.
In summary, the machining process includes design, CAD analysis, transmission, programming, process analysis, equipment preparation, processing, inspection and maintenance. Each link plays a vital role, and the accuracy of each link determines the quality and accuracy of the machined parts. Only by strictly following the machining process can we produce parts with stable quality and high precision.

Want to Learn More?
Advantages and Disadvantages of CNC Machining
Advantages
High precision: Precision machining can achieve high-precision machining, reaching sub-millimeter or even smaller precision requirements. Makes it very useful in manufacturing precision parts and equipment, such as aircraft engine parts, medical devices, etc.
Good surface quality: Precision machining can achieve a very high finish and flatness on the surface of the workpiece, which is essential for some parts with high surface quality requirements, such as optical components, molds, etc.
A wide range of processing materials: Precision machining can process a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, etc., so it has a wide range of applications in different fields.
Strong flexibility: Precision machining can be customized according to needs, is suitable for workpieces of various shapes and sizes, and has high flexibility
Disadvantages
High cost: The cost of precision machining equipment and process technology is relatively high, including equipment purchase cost, maintenance cost, and personnel training cost, which limits its application in some small and medium-sized enterprises.
Long processing cycle: Since precision machining requires multiple processes, as well as delicate debugging and testing processes, the processing cycle is long and cannot meet some projects with more urgent processing cycle requirements.
High energy consumption: Precision machining usually requires a lot of energy, especially high-speed machining and high-precision machining, which consumes a lot of energy and puts a certain amount of pressure on the environment.
High technical requirements: Precision machining requires operators to have a high level of technology and rich experience and requires high skills from operators, which also increases labor costs and training difficulties.
Dependence on equipment: Precision machining is highly dependent on advanced equipment and technology. Once the equipment fails or the technology is replaced, it may cause the production line to stagnate and production capacity to decline, which will have a certain impact on the company.
In summary, CNC machining offers unmatched precision, speed and reliability for many manufacturing needs, but it comes with higher cost and complexity. These trade-offs make CNC ideal when tight tolerances, durability and repeatability are paramount, and the higher equipment investment can be justified.
3D Priting VS CNC Machining
1. Differences in process principles
3D printing is an additive manufacturing technology, while CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing technology. To make the same object by design, 3D printing has less waste because the technology only requires the material needed to build the workpiece. In CNC, you need a block of material at least the size of the workpiece – a lot of material must be removed and is usually not recyclable.
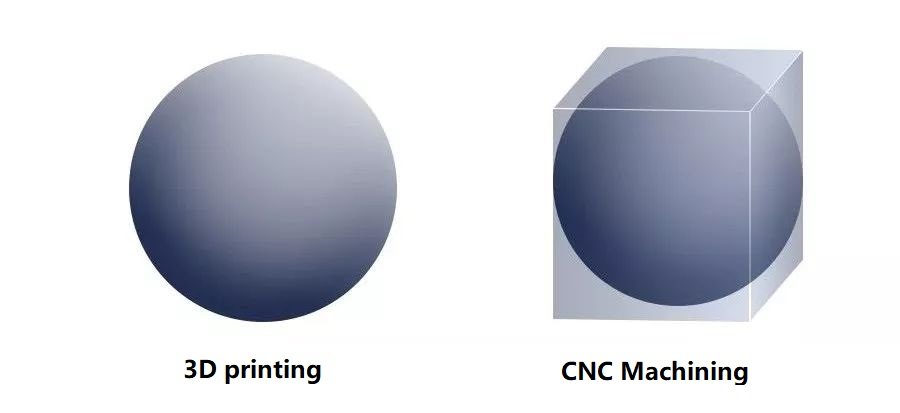
2. Differences in materials
3D Printing
The main 3D printing materials include liquid resin (SLA), nylon powder (SLS), metal powder (SLM), gypsum powder (full-color printing), sandstone powder (full-color printing), wire (FDM), plate (LOM), etc.
Among them, liquid resin, nylon powder and metal powder occupy the vast majority of the industrial 3D printing market.
CNC Machining
Commonly used materials for CNC machining include ABS, PC, POM, PP, acrylic (PMMA), bakelite, aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, stainless steel and other materials. It covers most of the types of products made on the market. However, the materials for 3D printing need to be specially developed, and the number of types lag behind CNC machining, especially the types of metal materials.
3. Differences in operating software
3D printing
3D printing slicing software is mostly simple to operate, and even laymen can use slicing software proficiently within one or two days under professional guidance.
Because slicing software is very easy to optimize and supports automatic generation, this is why 3D printing can reach individual users.
CNC Machining
CNC programming software is much more complicated and requires professionals to operate. People with zero foundation generally need to learn for about half a year, and a CNC operator is also required to operate the CNC machine.
Because programming is very complicated, a component can have multiple CNC processing schemes, while 3D printing will only place a small part of the processing time consumables, which is relatively objective.
4. Differences in post-processing
3D printing: There are not many options for 3D printing parts after processing, generally grinding, oil spraying, deburring, dyeing, etc.
CNC Machining: The options for CNC lathe parts after processing, in addition to grinding, oil spraying, deburring, there are also electroplating, silk screen printing, printing, metal oxidation, laser carving, sandblasting, etc.
Conclusion:
- CNC processing is suitable for medium and high quantities (less than 500 parts) and relatively simple models.
- For low quantities (or one-off prototypes) and complex, fine-structure models, 3D printing is the most suitable.
- For metal prototype models, CNC is price competitive, but the geometry is limited.
- When the quantity is large (mass production), other forming technologies are more suitable.
From the above four comparisons, 3D printing can easily produce complex structures and mixed material models. CNC has more advantages in material selection and large-scale model production. The two processing methods are complementary to each other. As an excellent service provider, our YP-MFG Factory not only provides CNC machining services but also a full set of services such as casting and forging, sheet metal fabrication, and aluminum extrusion to shorten your time with the product.
Tips on Choosing the Best Cnc Machining Manufacturers
Selecting the right CNC machining provider is crucial. Here are key factors to consider:
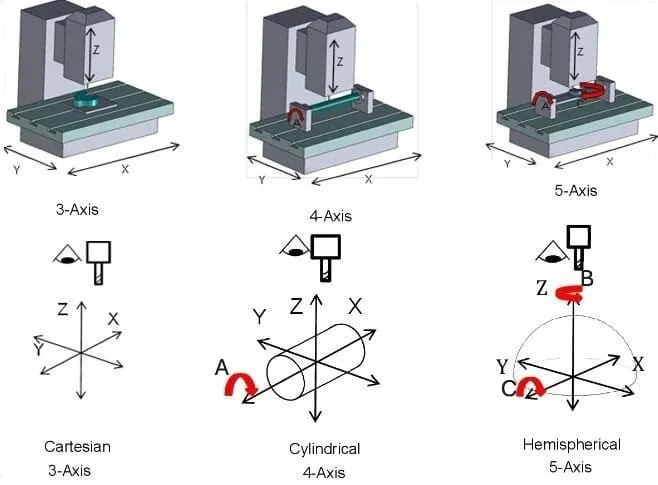
- Machine Capabilities: Ensure the manufacturer has the right type and size of equipment for your project. That includes the number of axes (3-, 4-, 5-axis), the type of machine (milling vs. turning), and the size envelope (travel limits) for your part. For very tight tolerances or complex shapes, look for advanced centers with multi-axis milling and live tooling.

- Material Expertise: Choose a shop experienced with your chosen material. Not all shops work with exotic metals or high-performance plastics. Verify they have successfully machined similar alloys or resins before. Discuss your material needs upfront.
- Quality and Inspection: High-precision machining demands strict quality control. Look for shops with certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and in-house inspection tools (CMMs, optical comparators). They should perform first-article inspections and provide certificates of compliance if needed.
- Turnaround and Scalability: Consider the supplier’s typical lead times and production capacity. Can they handle your order size – whether it’s prototype quantities or large batches – and deliver on your schedule? Good shops will be upfront about their throughput and will offer options like quick-turn or overnight machining if needed.
- Experience and References: Ideally, use a shop with a proven track record in your industry. For example, medical or aerospace parts may require knowledge of specific standards and tighter tolerances. Ask for references or case studies of similar projects.
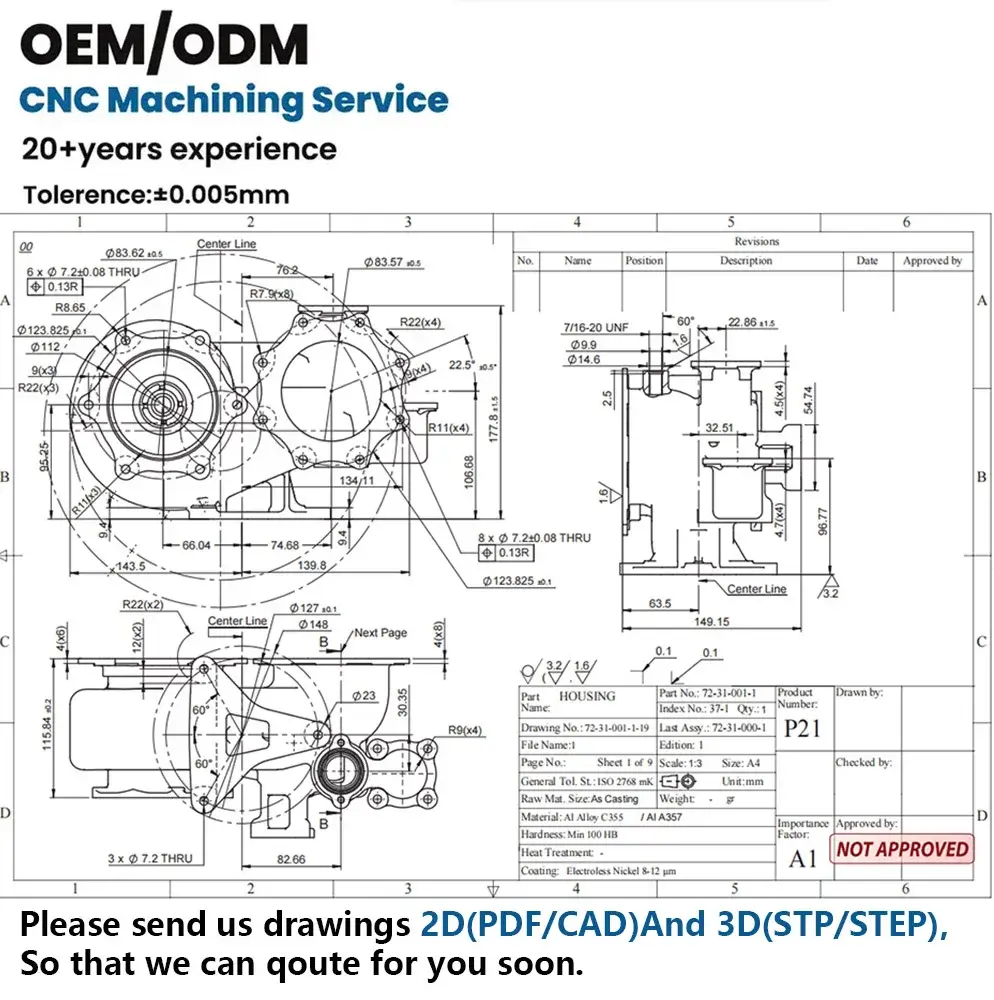
- Technical Support and Communication: A competent CNC supplier should assist with Design for Manufacturing (DFM) advice. They should review your CAD drawings and alert you to any potential issues (wall thicknesses, hole depths, tolerances). Good communication can save time and cost.
- Additional Services: Some providers offer secondary operations (heat treating, anodizing, assembly) and material sourcing. Bundling these services can simplify your project. However, ensure they have expertise in those areas if you require them.
- Cost and Value: Balance price against quality and service. The cheapest quote is not always best if it sacrifices precision or reliability. Conversely, very high cost requires justification (e.g., premium materials or ultra-tight specs). Ask for detailed quotes: a transparent shop will explain costs for materials, machine time, and finishing.
- Location and Logistics: If time is critical, local or regional shops reduce shipping time. Also, consider intellectual property – some sensitive designs are safer kept domestically.
By evaluating these factors – equipment, expertise, quality systems, and overall fit with your project – you can choose a CNC manufacturer that delivers the precision and service you need.
Is CNC Machining in Demand?
Yes. CNC machining remains in high demand globally due to its critical role in precision manufacturing. A 2023 market report projects the global CNC machine market growing from $67.5 billion in 2023 to $80.4 billion by 2028 (about 3.5% annual growth). This growth is driven by rising automation in manufacturing, especially in aerospace, automotive, electronics and medical industries where precision parts are needed.
On the labor side, skilled CNC machinists are actively sought. In the U.S., the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports an average of 14,000+ CNC machinist job openings per year (reference: https://www.bls.gov/). The demand for trained CNC operators/programmers remains strong because automation is increasing but still requires expert supervision and programming. As manual labor declines, companies rely on CNC expertise to maintain high-quality production.
In short, both market indicators and workforce data suggest CNC machining will continue to be a growing field. Its ability to deliver fast, precise, and consistent parts makes it indispensable. While there is a skills gap (some companies report shortages of qualified machinists), this also means good job prospects for trained personnel. Overall, CNC machining is in demand for high-precision, high-efficiency manufacturing applications.
CNC Machining Common FAQs
Q1: What is CNC Machining?
A: CNC Machining (numerical control machining) is a technology that uses computer programs to control machine tools to perform automatic cutting, turning, milling and other processing operations on materials, which can efficiently and accurately manufacture complex parts.
Q2: What is the difference between CNC machining and traditional manual machining?
A: Traditional machining relies on manual operation, with low precision and consistency, while CNC machining is controlled by computers and can repeatedly produce complex shapes with high precision, high efficiency and good consistency.
Q3: What are the common CNC machining equipment?
A: Mainly including: CNC milling machine, CNC lathe, CNC machining center (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis), CNC electric discharge machine (EDM), CNC grinder.
Q4: What materials are suitable for CNC machining?
A: Widely used in metals (aluminum, copper, steel, titanium, etc.), engineering plastics (POM, ABS, PEEK), composite materials, and even some ceramics and carbon fibers.
Q5: How high can the precision of CNC machining be?
A: Usually it can reach ±0.003mm, depending on the machine tool precision, machining technology and material properties.
Q6: How big a part can be produced by CNC machining?
A: The part size is limited by the machine tool worktable travel, and can be processed from tiny precision parts (millimeter level) to large structural parts (several meters long). The specific size needs to be confirmed with the supplier.
Q7: What factors determine the cost of CNC machining?
A: Mainly include: Material cost, processing time (complexity), surface treatment requirements, precision tolerance requirements, and production batch.
Q8: What information do I need to provide for a quote?
A:
Usually required:
3D drawings (STP, STEP, IGES format)
2D machining drawings (with dimensions and tolerances)
Material requirements
Surface treatment requirements
Quantity and delivery time
Q9: Can CNC machining replace 3D printing?
A: Both have their advantages and disadvantages. CNC has high precision and good strength, suitable for functional parts, 3D printing is suitable for rapid prototyping and complex internal structures. In many cases, the two technologies are used complementary.
Q10: What is the typical delivery time for CNC machining?
A: Depending on the complexity of the project, small batch samples can usually be delivered in 3-7 days, and mass production needs to be scheduled with the manufacturer.
Q11: Does it support on-demand small batch production?
A: Yes, many CNC manufacturers provide on-demand production services, supporting flexible orders from single pieces, small batches to large batches.
Q12: How to ensure the quality of CNC machined parts?
A: Reliable manufacturers usually have:
- ISO quality system
- Three-coordinate measuring equipment (CMM)
- Full inspection or random inspection report
- Strict production process management
Conclusion
As one of the cornerstones of modern manufacturing, CNC Machining, with its high precision, high efficiency and excellent consistency, continues to push all links from product research and development to mass production to a higher level. Whether in the fields of aerospace, automobiles, medical, electronics, or consumer goods, CNC machining is helping companies quickly realize complex designs and ensure product quality.
Looking to the future, with the development of intelligence, automation and digital twin technology, CNC Machining is constantly integrating the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analysis, and transforming towards more efficient, flexible and sustainable intelligent manufacturing. Shorter product launch cycle, better production cost control and stronger market competitiveness. Choose a trustworthy CNC machining partner to make your products more competitive!