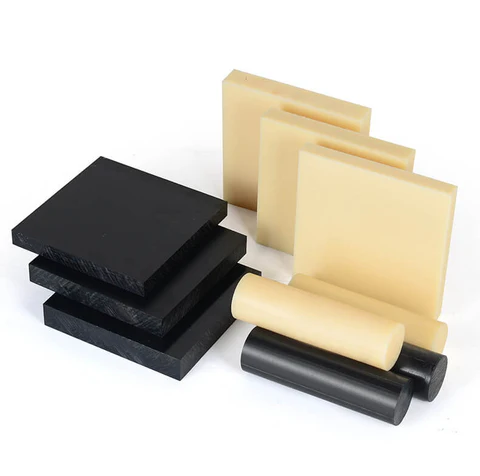
Plastic is a common non-metallic material with excellent insulation properties and low cost. Plastics are commonly used in the manufacture of electronics, electrical appliances, and automotive parts. When selecting a plastic material, factors such as its physical properties, mechanical properties, temperature resistance, and processability should be considered. This article will focus on a selection of plastic materials to provide a reference for your selection.
ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene)
ABS is a terpolymer of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, and is the most widely used polymer. It organically combines the properties of PS, SAN, and BS, offering excellent mechanical properties with a balanced balance of toughness, hardness, and rigidity.

Colors:
White, Black, Beige
Features:
ABS shares the common properties of its three components:
A makes it chemically and heat-resistant, and possesses a certain surface hardness. It is unaffected by water, inorganic acids, and food acids and alkalis, and can be used in temperatures ranging from -50 to +70°C. It has excellent impact resistance at low temperatures and good shape and dimensional stability at warm temperatures.
B makes it highly elastic and tough. It has high mechanical strength and rigidity, is scratch-resistant, and offers tensile strength, chemical resistance, and high surface strength.
S gives it the processing and molding characteristics of thermoplastics and improves electrical properties. It is easy to color, process, and electroplating, and has excellent chemical and electrical insulation properties.

Disadvantages:
Weakly weather-resistant and easily affected by weather conditions, has limited acid and corrosion resistance,soluble in ketones, softens in chlorinated hydrocarbons, fats, aromatic compounds, and aldehydes.
Applications:
Model materials, such as architectural models, figurines, food industry parts, electronic components for the imaging industry, and refrigeration. In the electronics and electrical industry, ABS can be used to manufacture components such as antenna sockets, coil bobbins, terminal blocks, converters, speakers, and connectors.
POM (Polyoxymethylene)
POM is a thermoplastic engineering plastic with a high melting point and high crystallinity. It is the hardest among thermoplastics and one of the plastic materials with mechanical properties closest to metal, commonly known as polyoxymethylene.

Colors:
Black, White
Features:
Resistant to organic solvents, insoluble at room temperature, with excellent low-temperature properties. Its heat deflection temperature is similar to that of PC/PTFE nylon and higher than PVC/PS/PE. It has high compressive strength, second only to fiberglass. It offers excellent wear resistance and creep deformation resistance, high rigidity, mechanical strength, and hardness, high dimensional and shape stability, and maintains toughness even at -400°C. It also has good sliding properties, is non-absorbent, and exhibits excellent wear, chemical, and hydrolysis resistance. It is naturally inert, suitable for food contact, and has excellent machinability.

Disadvantages:
It is not acid-resistant, especially mineral acid-resistant, is not UV-resistant, is not self-extinguishing, cannot be used near fire, and is not impact-resistant.
Applications:
Suitable for manufacturing sliding parts, precision mechanical components, water-resistant parts, dimensionally stable precision parts, and a wide range of components used in mechanical equipment. Examples include bearings, gears, impellers, cams, washers, bushings, guide rails, handles, and other fixture materials. Applications include automotive, electronics, medical, and food processing equipment.
Bakelite
Bakelite, also known as bakelite or phenolic laminate, is made from bleached wood pulp impregnated with phenolic resin and hot-pressed.

Colors:
Orange, Black
Features:
Excellent electrical properties at room temperature and good machinability. With a specific gravity of 1.45 and a warpage of ≤3‰, it offers excellent electrical, mechanical, and processing properties. It also possesses intermediate electrical insulation properties, is non-hygroscopic, non-conductive, and non-static, and is wear-resistant and high-temperature resistant.
Disadvantages:
Because bakelite products require heating during molding, processing time is longer than with ordinary plastics, mold wear is greater, and higher steel requirements are required.
Applications:
Suitable for insulating components in motors and electrical equipment requiring high mechanical properties. It can be used in transformer oil. It is also suitable for PCB drilling, silicone rubber molds, jigs, switchboards, electrical appliances, mechanical parts, communications equipment, and electrical insulation accessories.
Economic Benefits:
The raw material price of bakelite products is approximately 50% of that of ABS. Although bakelite products require heating during molding, which takes longer to process than ordinary plastics, and the molds are more worn and have higher requirements for steel, it is still the preferred alternative for many plastic parts due to its advantageous raw material prices.
PMMA (Plexiglas/Acrylic)
PMMA (Plexiglas), also known as acrylic sheet, is an important, early-developed plastic polymer material.

Color:
Colorless and transparent
Features:
High gloss, suitable for surface polishing, with a transmittance of 92% and a refractive index of 149, comparable to the best optical glass. It is thermally stable and suitable for temperatures ranging from -40°C to 90°C. It is UV-resistant, has excellent weathering resistance, and is resistant to inorganic acids, alkalis, lipids, hydrocarbons, and detergents. It exhibits tear resistance superior to other plastics. It has good electrical and dielectric properties and excellent mechanical strength.

Disadvantages:
It is susceptible to damage from stress cuts, has poor chemical and impact resistance, is brittle, and has short-term mechanical properties. Long-term use requires a tensile strength below 1500 psi to prevent brittle cracking. It has low impact resistance, and its toughness decreases with temperature. It is easily corroded by chlorinated hydrocarbons, aromatics, esters, and ketones.
Applications:
Machine covers and accessories, clock scales, fan blades, relay covers, windshields, electrical medical equipment, transparent models, specimens, ornaments, dentures, advertising nameplates, etc.
PP (Polypropylene)
PP, also known as PP, is a polymer formed by the addition polymerization of propylene. It is a white, waxy material with a transparent and lightweight appearance.

Color:
White
Features:
It has high stiffness, hardness, and surface strength, but its notched impact toughness is average. PP can withstand tensile stress and is easily welded. It is heat-resistant and maintains deformation in operating temperatures from +5°C to +100°C. It has good chemical stability and excellent electrical properties.

Disadvantages:
It has average oxidation resistance, average wear resistance, becomes brittle at low temperatures, has average notched impact toughness, can withstand tensile stress, but cannot be welded at high frequencies, has average adhesion to paint, and is susceptible to weathering.
Applications:
Pump and valve components, drinking water and sewage pipes, seals, spray coating carriers, electroplating processes, toy components, dental catheters, etc.
FR-4 (Epoxy Sheet)
FR-4 is a flame-retardant material grade designation, meaning that the resin must be able to self-extinguish after combustion.
FR4 epoxy sheet is a high-performance, multifunctional insulation material made from a high-temperature-resistant composite material and glass fiber.
Colors:
Green, Yellow, Black
Features:
Stable electrical insulation performance, excellent flatness, a smooth surface without pitting, and standard thickness tolerances. It offers high dielectric strength, heat and moisture resistance, excellent machinability, and structural stability. Its most notable feature is its high flame retardancy.
Applications:
Used in products requiring high-performance electronic insulation, as well as insulating components in motors and electrical equipment, such as FPC reinforcement sheets, PCB drilling pads, insulation boards for electrical (appliance) equipment, and insulation boards for electronic switches.
PA6 (Polyamide Resin/Nylon)
PA6, also known as nylon 6 or polyamide 6, is a high-performance compound. It offers superior overall properties, including mechanical strength, toughness, mechanical vibration damping, and wear resistance, making it commonly used in the manufacture of mechanical structural and maintainable parts.

Colors:
Black, White
Features:
Hard, with a low coefficient of friction, it is wear-resistant and pressure-resistant, dimensionally stable when dry, but exhibits increased ductility and toughness upon absorbing water, heat-resistant and thermally stable, highly tough, maintaining strength even at sub-zero temperatures, with high tensile strength and elastic modulus, excellent sliding and energy-absorbing properties, and excellent chemical resistance to many oils, fats, and mineral oils, good dielectric properties, making it easy to process, glue, and weld, and it is also an electrical insulator.
Disadvantages:
It absorbs water quickly, and its tensile strength and rigidity decrease with increasing temperature and humidity.
Applications:
Widely used in chemical machinery, gears and parts blanks for corrosion-resistant equipment, wear-resistant parts, transmission components, household appliance parts, automotive parts, screw machinery parts, chemical machinery parts, and chemical equipment.
PC (Polycarbonate)
PC is an amorphous, odorless, non-toxic, highly transparent thermoplastic engineering material in five-color or slightly yellowish hues, often called a transparent metal.
Color:
Colorless and transparent
Features:
A high-molecular-weight, low-crystalline plastic with excellent impact resistance, toughness, creep resistance, mechanical strength, and dimensional stability over a wide temperature range. It also offers transparency and ductility, weather resistance, and high-temperature resistance, suitable for temperatures from -150°C to +120°C. It is flame-resistant and radiation-resistant, with excellent insulation properties and strong steel-like strength, providing good electrical insulation.

Disadvantages:
Sensitive to dents and prone to cracking due to stress notches, reactive to hydrolysis and poor chemical resistance, easily scratched, difficult to polish, and poorly resistant to arcing, brittle after prolonged immersion in water, dissolution in hydrogen peroxide, and cracking due to corrosion by aromatics, copper, and acids.
Applications:
Widely used in high-tech fields such as insurance glass, slide projection equipment components, machinery and electronics, automotive, construction, household goods, and prototype materials. Currently, it has been used as windshields, bulletproof glass, observation windows of instruments, terminal blocks, jigs, models, etc. in aviation, electronics, and machinery.
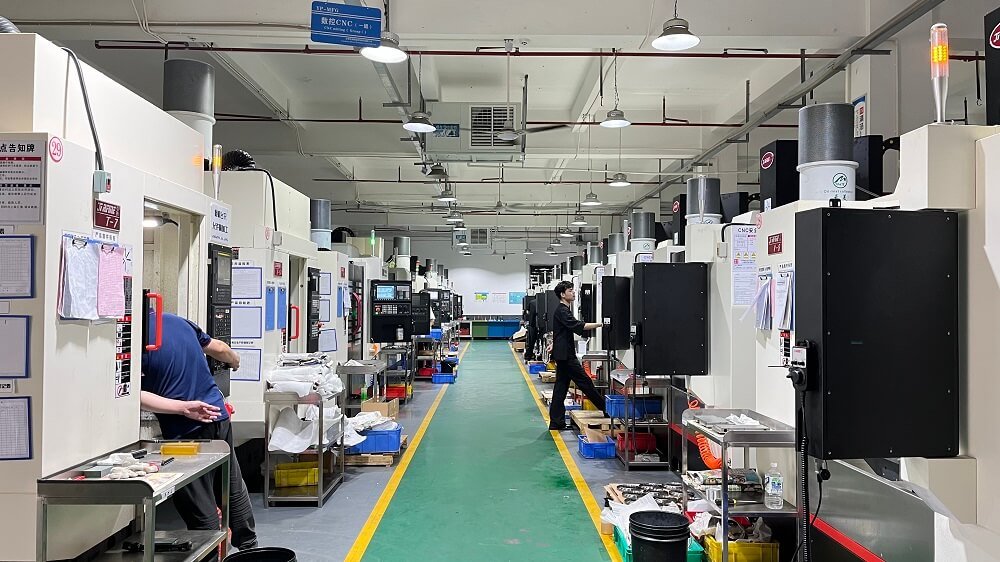
At YPMFG CNC Machining, we have extensive experience in plastics machining. We can select the most appropriate tooling, speed, and process parameters based on the specific material properties to ensure dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and consistent performance. Whether you’re working on functional prototypes, small-batch customizations, or complex structural parts, we provide high-precision, high-quality plastic CNC machining services, helping you quickly turn your designs into reality.






