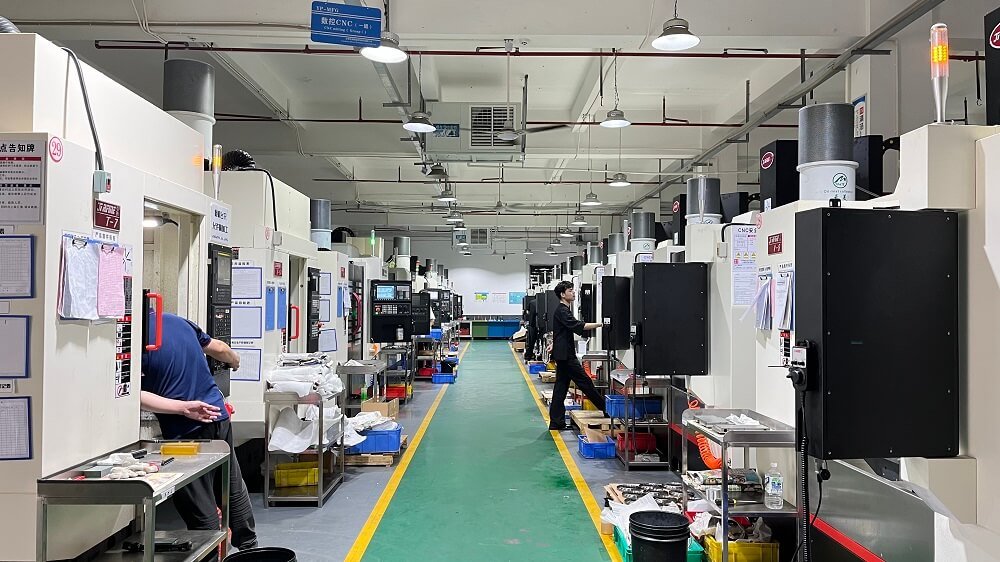
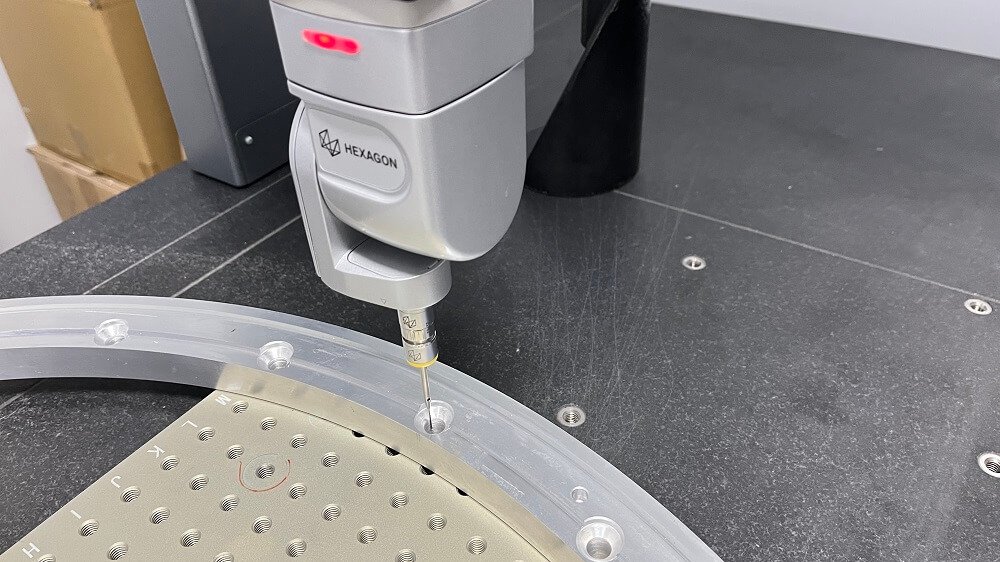
In the field of precision manufacturing, the surface quality of CNC machined parts directly affects both product performance and aesthetics. Scratches, a common surface defect, not only reduce the dimensional accuracy of workpieces but can also shorten their lifespan. So, how can scratches be effectively prevented in actual machining operations? This article provides an in-depth analysis from multiple perspectives.
Table of Contents
I. Main Causes of Scratches
In CNC machining, scratches are typically caused by mechanical friction, material properties, or improper process parameters.
Common causes include:
- Tool wear or improper geometry: A dull cutting edge can leave drag marks.
- Insufficient cutting fluid: Inadequate cooling and lubrication lead to friction.
- Improper clamping: The workpiece may be squeezed or damaged during clamping or release.
- Unclean environment: Dust or chips adhering to the tool or workpiece surface can cause scratches.
- Soft or sticky materials: These can easily be dragged by chips, leaving marks.

II. Key Measures to Prevent Scratches
1. Optimize Tool Selection and Maintenance
The tool directly contacts the workpiece, so its condition is critical. Regularly inspect tool wear, regrind or replace as needed. Use coated or specially alloyed tools to reduce friction and chip adhesion. Adjust tool geometry (e.g., rake and clearance angles) according to material type to ensure smooth cutting.
2. Set Proper Machining Parameters
Cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut are central to surface quality. Excessive parameters increase cutting force and risk of scratches, too low may cause vibration or excessive friction. Determine optimal combinations through testing and adopt layered cutting to minimize surface damage.
3. Enhance Cutting Fluid Application
Cutting fluids provide cooling, lubrication, and chip removal. Choose the appropriate type (oil-based or water-based) for the material, and ensure sufficient flow and pressure to minimize direct tool-workpiece contact and chip scratching.
4. Improve Clamping and Handling Methods
Scratches often occur during workpiece clamping or transfer due to uneven pressure or collisions. Use soft jaws (nylon or copper), protective pads, and standardized handling to ensure safe and gentle operation.
5. Maintain a Clean Working Environment
Metal dust, chips, and other hard particles can adhere to tools or surfaces, causing scratches. Regularly clean the machine table, tool magazine, and surrounding area—cleanliness is fundamental to preventing surface defects.
III. The Prevalence and Risks of Burrs
Burrs are excess metal residues formed at the edges of machined parts due to plastic deformation during cutting, grinding, or milling. They are an unavoidable byproduct of metal processing.
Burrs not only compromise appearance but also hinder assembly, degrade performance, accelerate wear, and reduce service life. With higher product precision demands, deburring has become increasingly critical. Severe burrs can even render entire assemblies unusable.
IV. Methods for Burr Removal
Currently, burr removal requires an additional post-machining step. The main approaches fall into two categories—chemical and physical:
Chemical Deburring
A soaking process originating in Germany, chemical deburring uses controlled reactions to remove burrs based on structural differences between the burr and the base material.
It’s widely used in automotive, aerospace, and precision machining industries, for components such as gears, bearings, pumps, fasteners, and CNC parts.
Suitable for burr thicknesses under 0.2 mm, this process offers superior reliability, consistency, stability, and environmental safety compared with traditional methods. It improves surface finish, saves time, and enhances corrosion resistance.
Physical Deburring
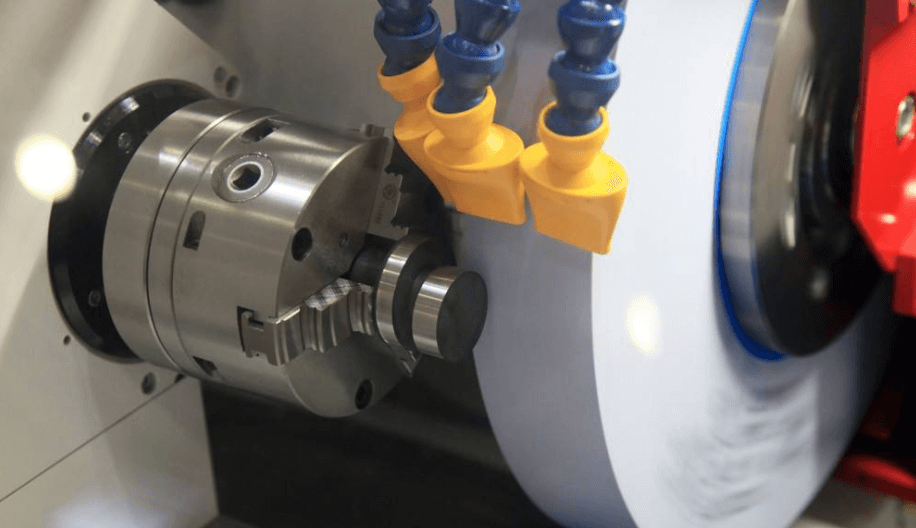
Includes mechanical cutting, grinding, filing, scraping, sanding, polishing, and automated brushing.
While effective for simple geometries and low-precision parts, results can be inconsistent, and labor costs are high.
When selecting a deburring method, consider material properties, part geometry, size, precision, surface roughness, dimensional tolerance, deformation, and residual stress.
V. How to Prevent Burrs and Tool Marks in Machining
To ensure final product quality, preventing burrs and tool marks is essential. Key practices include:
1. Select the Right Cutting Tool:
Sharp, smooth-edged tools minimize burr formation and surface friction.
2. Adjust Cutting Parameters:
Optimize cutting speed, feed rate, and depth to match material properties. Perform trial runs to find the best settings.
3. Use Suitable Coolants:
Coolants reduce friction and heat, lowering tool wear and preventing burrs.
4. Maintain Tool Sharpness:
Regularly grind or replace tools to keep edges sharp and avoid burr-causing deformation.
5. Employ Chip Removal Systems:
Efficient chip evacuation prevents chip adhesion and subsequent burr formation.
6. Pre-process Workpieces:
Remove rust or pre-existing burrs before machining to reduce secondary defects.
7. Use Vibration-Assisted Machining (if applicable):
Reduces cutting resistance and burr formation for specific materials.
8. Apply Finishing Processes:
Grinding, polishing, or superfinishing can enhance surface quality and eliminate minor tool marks.
By combining these strategies, manufacturers can effectively minimize burrs and scratches during machining, thereby improving both quality and efficiency.
Ⅵ. Conclusion
In CNC precision machining, surface quality control is a key indicator of process stability. Through scientific tool management, optimized process parameters, proper coolant selection, and standardized operation, scratches and burrs can be effectively prevented.
For micro-burrs already present, chemical or physical removal methods can be selected according to part type to achieve higher precision and superior finish quality.
At YP-MFG Machining, we focus on precision manufacturing and surface process optimization, leveraging advanced CNC technology and strict quality control to help clients achieve higher accuracy and better surface finishes in their parts.






