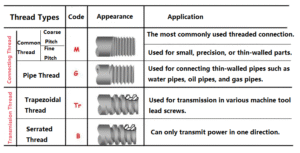
450 essential machining questions and answers in this comprehensive guide. A must-have reference for engineers seeking practical knowledge, tips, and troubleshooting advice in manufacturing.
1. The main forms of structures are: frame structures, container structures, box structures, and general member structures.
2. Riveter operations can be divided into the nature of the process: preparation, release, processing, molding, assembly and connection.
3. Metal structure connection methods are: riveting, welding, riveting and welding hybrid joint, and bolt joint.
4. In the machine manufacturing industry, riveter belongs to the hot processing category.
5. Thermal processing: all or part of the metal material heating, processing molding.
6. The honed frame structure is (profile) as the main body of the structure, manufactured.
7. The container structure is (plate) as the main body of the structure, manufactured.
8. The box structure and general structure are a mixture of (plate) and (profile) manufacturing structures.
9. Stock preparation is the preparation of raw materials and part blanks.
10. Steel plates and sections can be deformed during transportation, lifting, and storage.
11. Steel deformation will affect the parts of the (lifting, under the material, gas cutting) and other processes, normally.
12. Parts in the processing of deformation, if not corrected, will affect the correct assembly of the structure.
13. Welding deformation will reduce the assembly (precision), so that the steel structure within additional stress, affecting the strength of the components.
14. The deformation of flat steel is: bending, twisting, and compound deformation.
15. The multi-roller correction machine, according to the arrangement of the shaft rollers and the adjustment of the position of the rollers, can be divided into: the upper and lower rollers parallel correction machine, the upper and lower rollers tilt correction machine.
16. Flame correction of the heating mode: point, line, triangle heating.
17. The effectiveness of flame straightening is determined by (position of heating and the temperature of heating).
18. The methods of correction are: mechanical correction, manual correction, flame correction, and high-frequency heat reaming.
19. Release and numbering are the first steps in the process of making a metal structure.
20. Release and number: will directly affect the quality of the product on the production cycle, and cost has a direct impact.
21. The common measurements used for layout are: wooden folding ruler, straightedge, steel tape measure, steel plate ruler, etc.
22. Sample commonly used tools are: scratch gauge, ground gauge, sample punch, scratch needle, and small hand hammer.
23. The procedure of real size sampling is: line sampling, structure sampling, and unfolding sampling.
24. The contents of the unfolding sample are: plate thickness processing, unfolding drawing, and making a number of material samples.
25. According to its use, the sample is divided into: the number of material samples, checking samples, and positioning samples.
26. The production of samples is generally used: 0.5 ~ 2 mm thick iron.
27. samples, sample rod drawing method: straight line drawing method, transition drawing method.
28. How to achieve a reasonable use of materials?
A: To centralize the nesting and utilization of residual materials.
29. A curve is divided into a plane curve and a space curve.
30. the real length of the straight line segment method: rotation, right triangle method, the branch method, and the method of surface change.
31. The steps of unfolding are: through the geometry of the first line, the real length of the line, the section of the real shape, and then unfolding the map.
32. The basic methods for finding three-dimensional intersections of planes are: the prismatic method and the prismatic method.
33. The basic methods for finding three-dimensional intersections of surfaces are meridian and latitudinal.
34. The main methods for solving coherent lines are: the auxiliary plane method, the plane line method, and the spherical method.
35. What are the characteristics of coherent lines?
Answer:
(1) A coherent line is the common line of the two intersecting forms and the line of demarcation.
(2) Because the form has a certain range so the coherence line is always closed.
36. Intersecting lines: the intersection of intercepted planes and three-dimensional surfaces.
37. Prime line: the mother line in any position on the surface of the component is called a prime line. 38.
38. Common methods of unfolding are: parallel line method, radial line method, triangle method.
39. The spherical surface of the division of the way usually has: sub-band method, block method, split flap method.
40. The main content of plate thickness treatment is to determine the neutral layer of the bending parts and eliminate plate thickness interference.
41. Angle steel bending parts of the material length according to (center of gravity layer).
42. shear straight line of the shearing machine: gantry beveling shear, cross wood beveling shear, combined punching and shearing machine.
43. Shear curve of the machine: disc shear, vibration shear.
44. What are the characteristics of vibratory shears?
A. Vibratory shears are capable of shearing a variety of curves and bores.
45. Joint shear punch machine tool by (oblique mouth shear, steel shear, small punch).
46. Try to analyze the transmission order of the shearing machine: the original moving parts → transmission parts, → workpiece.
47. The gantry shearer front and rear gear plate has: positioning role.
48. In the gantry or beveled shear bed, positioning shear: shear plate positioning shear, rear baffle positioning shear, baffle positioning shear.
49. The beveled shear on the material shear force can be decomposed into: shear force, horizontal tension, and off the mouth.
50. Shearing machine: not suitable for cutting alloy materials and hardened materials.
51. The cutting oxygen pressure should be based on: the thickness of the workpiece, the torch nozzle aperture, and the purity of oxygen to be used.
52. The ignition point of carbon steel in oxygen is 1100℃~1150℃.
53. The gas cutting conditions for metal materials are: pure iron, low carbon steel, medium carbon steel, and ordinary low alloy steel.
54. The process of gas cutting is: preheating of the metal, burning of the metal, oxides are blown away.
55. What is the function of a round plate tooth? What are the components?
A: It is a tool used for machining external threads and consists of a cutting part, a positioning part and a chip removal hole.
56. What is the form of beveling related to?
A: With the type of material, thickness, welding method, and mechanical properties of the product.
57. Grinding: grinding wheel on the surface of the workpiece is called grinding.
58. Grinding tools are mainly: wind turbines and electric grinders.
59. Bending process molding process, what will happen to the steel deformation?
A: Elastic deformation and plastic deformation will occur. 60.
60. Riveters commonly use bending molding methods: cold bending, hot bending, hand bending, and mechanical bending.
61. Compression bending molding material bending deformation: free bending, contact bending, correction bending.
62. In the bending process of the material’s cross-section shape changes with relative bending radius, cross-section geometric characteristics, and bending method.
63. Preventing the bending process of the blank deflection is the method: a support device and positioning holes.
64. Bending machine tools include: plate rolling machine and section bending machine.
65. The main processes of manual bending: scribing, sand filling, heating and bending.
66. metal structure of the coupling method: rivet coupling, threaded coupling welding three.
67. Selection of coupling methods to consider: the strength of the member, the working environment, materials, construction conditions and other factors.
68. Riveted joints in the form of: butt joints, corner joints lap joints.
69. Solid rivet head form: semi-circular head, countersunk head, semi-countersunk head.
70. The main AC arc welding machines are: BX1-330 and BX-500.
71. The basic process of hot riveting is: fastening of the riveted part, hole trimming, heating of the rivet, jointing and threading of the nail, jacking of the nail and riveting.
72. The types of riveting are: strong riveting, dense riveting, and tight riveting.
73. The tools used to repair holes are: a reamer.
74. Threaded joints commonly used anti-loosening measures are: increasing friction, mechanical anti-loosening.
75. Welding arc by: anode area, cathode area and arc column.
76. welding machines: DC welding machines and AC welding machines.
77. Local deformation: refers to a part of the member of the deformation, including angular deformation, wave deformation, local convexity and concavity.
78. Welding according to the space position: flat welding, vertical welding, horizontal welding, and back welding.
79. Welding process, the electrode has which three directions of movement?
A: There are three molten pool direction movements: moving along the welding direction, lateral swing.
80. The three elements of assembly are: positioning, support and clamping.
81. Manual clamps are: screw clamps, wedge clamps, lever clamps, and eccentric clamps.
82. Non-manual clamps: pneumatic clamps, hydraulic clamps, magnetic clamps.
83. Screw clamps have: clamping, pressure, top, support and other functions.
84. Common measurements used in assembly are: linear dimensions, parallelism, perpendicularity, coaxiality, and angles.
85. Workpiece in the assembly of the form of support: assembly platform support, assembly tire frame support.
86. Assembly tire rack, according to its function, can be divided into: general-purpose tire rack and special tire rack.
87. Assembly commonly used positioning methods are: scribing positioning, sample positioning, and positioning elements positioning.
88. The basic methods of plane intersection are: the prismatic method and the prismatic method.
89. Hot riveting generally consists of four people. What is their division of labor?
A: a person to heat, transfer, a person to receive the nail through the nail, a person to top nail, a person riveted.
90. What is the purpose of the flat end in a tapered shank drill?
A: It is used to increase the torque transmitted and to prevent the drill from striking out in the spindle hole or drill sleeve.
91. What is the function of the guide portion in a drill?
A: It keeps the drill bit in a straight drilling direction during the cutting process. It also serves to polish the walls of the hole and serves as a backup to the cutting part.
92. What undesirable phenomena occur when the hole is about to be drilled through?
A: When the drill bit just drilled through the workpiece when the axial resistance is suddenly reduced, due to the clearance of the drilling machine feeding machinery and elastic deformation of the sudden recovery, will make the drill bit with a large amount of feed automatically cut, resulting in the breakage of the drill bit or reduce the quality of the hole drilled.
93. What is the role of the cutting fluid when drilling?
A: Reduce friction, reduce drill resistance and cutting temperature, improve the cutting ability of the drill and the surface quality of the hole wall.
94. Cutting volume: is the cutting speed, feed, and depth of cut in general.
95. Grinding: The grinding wheel is on the surface of the workpiece, processing methods.
96. Unfolding: the surface or part of the metal structure according to the actual shape, the size of the process of spreading in a plane, called unfolding.
97. The methods of unfolding are: parallel lines, triangles, and radial lines.
98. The parallel line method is based on the condition that the lines on the surface of the member are parallel to each other and reflect the real length on the projected plane.
99. Plate thickness treatment includes: determining the neutral layer of the bent part and eliminating plate thickness interference.
100. Changes in the location of the neutral layer of the plate thickness are related to: the bending radius of the plate and the thickness of the sheet.
101. The general principles of plate thickness treatment for coherent members are: the length of the unfolding is based on the size of the neutral layer of the member, and the height of the curves in the unfolding plan is based on the height of the contact point of the member.
102. The main content of the sample is: plate thickness processing, unfolding diagram and according to have made a component unfolding diagram to produce a number of material samples.
103. riveters commonly used shearing equipment: gantry shears, beveling shears, disc shears, punching shears combined punching and shearing machine.
104. Rolling machines, according to the number of rollers and the arrangement of forms, can be divided into: symmetrical three-roller, asymmetrical three-roller, and four-roller.
105. Punching die according to the structure can be divided into: simple mold, with a guide column mold, and composite mold.
106. The structure of the composite blanking die is characterized by: with both the role of the drop convex die, and the role of the punching concave die convex-concave die.
107. Punching force refers to the maximum resistance of the material to the die when punching.
108. The deformation process of sheet separation during punching can be divided into: elastic deformation stage, plastic deformation stage and shearing stage.
109. Minimum bending radius: the smallest value of the bending radius that can be bent without damage to the material.
110. Reduce the springback of the press-bent parts. The common methods are: corrective mold method and pressurized correction.
111. The purpose of using a crimping ring in stretching is to prevent the edge of the stretched parts from wrinkling.
112. Crank press crank linkage mechanism, what role?
A: It can not only make the rotary motion into reciprocating linear motion, but also play a role in amplifying the force.
113. Hand forming for sheet metal workers includes: bending, arching, edge pulling, crimping, nipping, and straightening.
114. Spreading samples can be used for: numbering, making separation molds and making milling samples.
115. Edge Release: The operation of stretching and thinning the material at the edge of a deformed part during the molding process is called edge release. Forming methods are thinning and pulling thin.
116. Edge pulling: the use of wrenching and edging methods, the edge of the sheet material will be processed into a curved workpiece.
117. Crimping: In order to increase the rigidity and strength of the edge of the workpiece, the edge of the workpiece is curled, called crimping.
118. Bite: the edge of the two pieces of sheet material or a piece of sheet material on both sides of the folded bite, and press them together, known as the bite.
119. Plate thickness treatment: in order to eliminate the influence of plate thickness on the shape and size of the unfolded drawing, and the methods adopted.
120.The general steps for calculating the unfolded length of a bent part are: dividing the bent part into straight and circular segments, calculating the lengths of the segments separately, and adding the calculated lengths together.
121. Under what circumstances should notching down of profiles be applied?
A: Angles, channels, I-beams bent into folded corners
122. The whole punching process is divided into: elastic deformation stage, plastic deformation stage, and shearing stage.
123. Punching: the use of punching templates will be part of the sheet and the other part of a certain closed line along the stamping process to separate from each other.
124. Bolt coupling: there are two kinds of: bearing axial tensile planting role of the coupling, bearing transverse role of the coupling.
125. Bolt coupling measures to prevent loosening: increase friction, mechanical anti-loosening.
126. Mechanical anti-loosening: cotter pins, check washers, stop washers, tandem steel wire.
127. Welding arc: in the gas medium between the two electrodes to produce a strong and persistent discharge phenomenon.
128. Welding arc consists of: cathode area, anode area, and arc column.
129. What are the three directions of motion of the welding electrode?
A: to the direction of the molten pool, along the welding direction, for lateral swing.
130. Welds can be categorized according to their spatial position: flat, vertical, transverse, and backward welds.
131. What are the properties of a coherent line?
A: It is both the common and dividing line between the surfaces of two forms, it is always closed in space.
132. Coherent line: a member consisting of the intersection of two or more geometries.
133. Factors affecting the quality of blanking are: die clearance, the convex-concave die centerline does not coincide, the die working edge wears blunt.
134. The general principle of mold design is: in order to ensure the quality of stamping under the premise of striving for the design of the mold, easy to manufacture, simple technology and low cost, easy to use.
135. The purpose of calendering force is to select the calendering equipment correctly.
136. Free bending: when the end of the bending convex mold, blank, and concave mold mutual coincidence no longer occurs after the impact.
137. Corrective bending: refers to the convex mold, blank, concave mold, and three after the coincidence of another impact, the bending of the part to play a corrective role.
138. What defects are easily produced when pressing the head?
A: Wrinkling and puckering, straight edge draw marks, indentation pits, micro-cracks on the outer surface, longitudinal tearing, deflection, ellipse and inconsistency in the size of diameters.
139. Expansion joint: the use of a tube and a tube plate deformation to achieve sealing and tightening of the coupling.
140. The purpose of calculating punching force is for the rational selection of equipment capacity and the design of dies.
141. What methods can be used to reduce the punching force?
A: Beveled edge punching dies, step punching dies, and heated punching dies.
142. The purpose of calculating the bending force is to select a bending press and design a mold.
143. What is included in the degree of tensile deformation?
A: the degree of sticking of the mold, the degree of deformation allowed by the material to pull shape.
144. How to determine the number of times the workpiece is pulled?
A: Based on the maximum deformation and material elongation of the workpiece being pulled.
145. How to determine the coefficient of pull form?
A: Depends on the material properties, pulling angle, friction coefficient and whether the prefabricated pulling.
146. Brittle materials such as high carbon steel, high alloy steel and cast iron are not suitable for cold work straightening.
147. When the complex deformation of the angle steel when, its positive order is: first to correct the distortion, then correct the bending, and finally correct the angular deformation.
148. Causes of deformation of steel structure: one is caused by external forces, and internal stresses cause one.
149. Elimination of welding residual stress methods are: overall high-temperature tempering, local high-temperature tempering, temperature difference stretching method, mechanical stretching method, vibration method.
150. Welding overall deformation refers to the shape and size changes that occur in the entire structure.
151. Hammer spreading method: elongation of the fibrous tissue of the sheet metal by hammering.
152. Rivet stem length: determined by the total thickness of the connected parts, the gap between the nail hole and the nail stem diameter, the riveting process and other factors.
153. The rivet head is too small after riveting because the nail rod is shorter or the hole diameter is too large.
154. Welding according to the metal in different states can be divided into: fusion welding, pressure welding, and brazing.
155. Melt welding: the use of local heating to bring the welded joints to the melting state of the method.
156. Clamping: that is, with the help of external forces, so that the positioning of the parts is fixed, so that its position in the process remains unchanged.
157. Six-point positioning rule: six positioning points are used to limit the freedom of the part in space, in order to seek to determine the spatial position of the part completely.
158. Relative parallelism: the parallelism of the measured line or surface on the part with respect to the measurement reference line or surface.
159. Relative perpendicularity: refers to the measured lines or surfaces on the part, relative to the measurement datum or the degree of perpendicularity.
160. Assembly fixtures used in assembly: assembly tools, assembly fixtures, assembly spreader.
161. Commonly used assembly hoists are: wire rope, chains, hand hoists, and special hoists.
162. How many types of guides are there for blanking dies?
A: There are two types of guide pillars, guide sleeves and guide plates.
163. How many parts are there in a blanking die?
A: It consists of a working part, a material positioning part, an unloading part and a die base.
164. What is the function of the clearance of the drawing die?
A: To reduce the friction between the material and the die and to control the flow of material in the cavity of the die.
165. The structure of the bite can be divided into: vertical single bite, vertical double bite, horizontal flat bite and various corner bites.
166. When the external force is removed, what is the reason for the rebound of the bent parts?
A: It is because when bending by hand, the outer surface of the sheet is stretched and the inner surface is pressurized, so it produces rebound.
167. Cold arching is obtained by shrinking the edges of the sheet and spreading the center of the sheet, and hot arching is obtained by heating the sheet to shrink it.
168. There are two methods of edge pulling, one with a general-purpose tool and the other with a type of tire.
169. Edging: Edging is the process of first wrinkling the sheet and then flattening the wrinkled area to prevent stretching and recovery, thus reducing the length of the sheet being contracted and increasing the thickness.
170. The basic principle of hemming is: for the forming of convex curved edge workpieces, it mainly involves the bending of the outer edge of the flat edge of the material to shrink and thicken and shorten, forcing the vertical edge to curve shape.
171. The purpose of correction is: through the application of external forces or local heating so that the longer fibers shorten, the shorter fibers elongate, and ultimately make the layers of fibers converge to achieve the purpose of correction.
172. The principle of flame straightening is: the use of local heating of the metal deformation to offset the original deformation, to achieve the purpose of correction.
173. Factors affecting the effect of flame correction are: the rigidity of the workpiece, heating position, flame heat, heating area, and cooling mode.
174. The heating mode of flame correction: point, line and triangle heating.
175. Factors in determining process margins are: the effect of release errors, the effect of errors during part machining, the effect of assembly errors, the effect of weld distortion, and the effect of flame straightening.
176. Samples according to their use can be divided into: the number of material samples, molding sample, positioning sample and sample rod.
177. Drawing method: direct drawing method and transition drawing method.
178. How to choose the general release of the reference line?
A: Two mutually perpendicular lines or surfaces, two centerlines as a reference line, a plane and a centerline as a reference.
179. Sampling tolerance: in the process of sampling, due to the sampling gauge and tool precision and the level of operation and other factors, the actual sample of the map will exhibit a certain size deviation, the deviation is controlled within a certain range, called sampling tolerance.
180. Structural sampling includes: determining the combination position and connection form of each part, making necessary changes according to the actual production and processing capacity, calculating or measuring the length of the parts and the actual shape of the plane parts, and designing the tire or tire carrier.
181. The following methods are used to find the real length of a line segment: rotation, right triangle method, transposition, and branching.
182. What is the graphing rule for finding the real length of a line segment by the right triangle method?
A: It is to use the projection of the line segment on any projected surface as a right-angled side of a right triangle, and the corresponding projection for the surface perpendicular to the axis of the length of the projection as a right-angled side of the other, the hypotenuse is the real length of the line segment.
183. Rotation method to find the real length: that is, the general position of the space around a fixed axis of rotation, into a parallel line, the projections of the line in the projected surface parallel to it reflect the real length.
184. The real length of the curve for the method: the method of surface change, the expansion method.
185. Changing surface method: it is to set a new projection surface parallel to the curve, then the projection of the curve on the surface reflects the real length.
186. Unfolding method: is a curve in the view of a length straightened, while maintaining the height of the other view of the same, made by the unfolding of the line that is sought.
187. The basic characteristics of intercepts are: intercepts must be a plane figure enclosed by a closed line or curve, intercepts are common to the intercept plane and the surface of the cubic plane, and are formed by a collection of points that are on both the intercept plane and the surface of the cubic plane.
188. The methods of finding three-dimensional intercepts are the prismatic plane method and the prismatic line method.
189. The methods of finding three-dimensional intercepts of surfaces are: the plane line method and the latitude line method.
190. What are the characteristics of a coherent line?
A: First, it is a line common to the surfaces of two intersecting forms, and it is also a line of demarcation between the two intersecting forms, second, it is a line of coherence that is closed.
191. The essence of finding the line of coherence is to find a certain number of common points on the surfaces of the two forms, and to connect these common points in order.
192. The choice of method of coherence is the principle of selection: with the plain line method for coherent line should be known at least one projection of the coherent line, with the auxiliary plane method for coherent line, the intersection line should be the simplest geometric figure, spherical method is only applicable to the rotating body coherent, and the axes of the components of the intersection.
193. Under what conditions is a line of coherence a plane curve? Under what conditions is a coherent line a plane curve, and the front projection of a curve is two intersecting lines?
A: When the two tangent to the same sphere of any rotary body coherent, the coherence line is a plane curve. At this time, when the two rotating body axes are parallel to the basic projection surface, the projection of the coherence line is the intersection of the two straight lines.
196. Straight surface: Does the straight line form the surface as the mother line?
197. What are the characteristics of a cylindrical surface?
A: All the lines are parallel to each other. when a cylindrical surface is sectioned by planes parallel to each other, the section pattern is the same.
198. What are the characteristics of a conical surface?
A: All the principal lines intersect at one point. when the taper is cut through planes parallel to each other, the section patterns are similar, the intersection line across the top of the taper is triangular.
199. Pull form, the plastic deformation process of the material is divided into: material bending, material tensile deformation, and complementary pull.
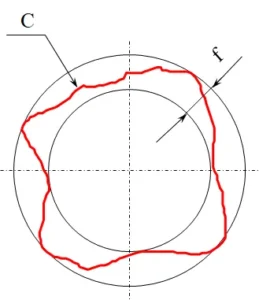
200. Pull form: is the plate material in the state of tension, so that it is in accordance with the ideal surface and plastic deformation, and to overcome the rebound of the molding method.
201. Plate thickness treatment includes: determining the neutral layer of the bent part and eliminating plate thickness interference.
202. The plate thickness neutral layer position changes with the plate bending radius and sheet thickness.
203. The general principles of plate thickness treatment for coherent parts are: the unfolding length is based on the size of the neutral layer of the member, and the height of the curve in the unfolding drawing is based on the height of the contact of the member.
204. The main content of the sample is: plate thickness processing, unfolding diagram and according to have made a member of the unfolding diagram to produce the number of material samples.
205. Riveters commonly used shearing equipment: gantry shears, shears, disc shears, punching shears, combined punching and shearing machine.
206. Rolling machines, according to the number of rollers and the arrangement of forms, can be divided into: symmetrical three-roller, asymmetrical three-roller, and four-roller.
207. Punching die according to structure can be divided into: simple mold, with a guide column mold, and composite mold.
208. The structure of the composite blanking die is characterized by: with both the role of the drop convex die, and the role of the punch concave die convex and concave die.
209. Punching force refers to the maximum resistance of the material to the die when punching.
210. Rebound: The phenomenon of the material returning due to its elasticity after the removal of an external force during the bending process is called rebound.
211. Stretching: A method of stamping process in which a sheet is made into an open hollow part by using a press and a corresponding die.
212. Stretch Coefficient: The ratio of the area of the section of a material after each stretch to the end area before the stretch is known as the stretch coefficient for that stretch. The tensile coefficient actually reflects the size of the degree of deformation of the stretched parts.
213. Crimp ring: In the stretching process, in order to prevent the workpiece mouth edge part from destabilization and wrinkle, a concave, convex die is used between the edge part of the set of the ring-shaped compression device.
214. Friction presses work on the principle of contact transmission between the flywheel and the friction disk, and work by means of the principle of relative motion of the screw and the nut.
215. What are the advantages of friction presses?
A: Faster action can make the slide stop at any position within the stroke, once overloaded, only caused by the flywheel and friction disk sliding between, without damage to the machine parts.
216. What are the advantages of the stamping process?
A:
(1) High productivity. One stroke of the press can complete a process, and sometimes multiple processes.
(2) High material utilization.
(3) The same product stamping parts of the same shape and size, with good interchangeability.
(4) Simple operation, easy to realize mechanization and automatic production.
217. Stamping process: separation process, forming process, composite process.
218. Punching: the use of punching dies in the press to separate the sheet in a stamping method.
219. How to distinguish between punching and dropping?
A: In general, the sheet is punched to form two parts, namely, the punched-off part and the part with holes. If the purpose of punching is to produce a certain shape of the workpiece, i.e., punching down the part for the need is called drop material, on the contrary, the purpose of punching is to process a certain shape of the hole, punching down the material for the cost of the material is called punching.
220. When punching, what are the stages of the material separation process?
A: Elastic deformation, plastic deformation, and separation by cracking.
221. Methods to reduce the punching force include: beveled edge punching, stepped convex die punching, and blank heating punching.
222. Minimum bending radius: material in bending, without damage to the minimum limit value of the bending radius, known as the minimum bending radius.
223. External forces that cause deformation of a structural member include: bending force, torsion, impact, tension and pressure.
224. What can external forces cause to occur within a member? When external forces are removed, some of the internal forces may remain, creating what?
A: External forces may cause internal forces to appear inside a member, when the external forces are removed, internal stresses are formed.
225. What is the welding process, and what is it a process for metal structural members? What is the main cause of deformation of the member?
A: It is an uneven heating and cooling process, it is the main cause of deformation due to internal stresses in the member.
226. In which directions does the shrinkage of the weld and the metal near the weld mainly occur?
A: Shrinkage in both longitudinal and transverse directions.
227. Factors that may cause deformation of structural components in terms of design include: the rationality of the structure, the position of the weld, the form of the weld bevel, etc.
228. Factors that may cause deformation of structural components in terms of technology include: welding procedure, welding sequence, anti-deformation measures, etc.
229. How to be the premise of quality and quantity to complete the corrective work: correct judgment and selection of the corrective position.
230. Analyze the causes of deformation of components, to distinguish what causes deformation.
A: To distinguish whether external forces or internal stresses cause the deformation.
231. The deformations of a work-shaped sorghum are: arch deformation, side bending, and corner deformation.
232. The deformations of box sorghums are: arch deformations, twisting.
233. What is the main conflict when two deformations of box sorghum occur simultaneously? In what order should the correction be made?
A: Distortion is the main contradiction, and should be carried out in the order of first distortion and then arch deformation.
234. Internal force: At the same time that an external force deforms an object, a force appears within it to resist the deformation, which is called internal force.
235. Stress: The internal force that appears per unit of cross-sectional area when an object is subjected to an external force is called stress.
236. Internal stress: When there is no external force, the stress that exists inside the object is called internal stress.
237. local deformation: a part of the component deformation, called local deformation.
238. Overall deformation: the shape and size of the whole component change, called the overall deformation.
239. Shrinkage deformation: one of the basic forms of deformation, mostly refers to the object after heating and cooling, the size of the shortening deformation of deformation.
240. Twisted deformation: one of the basic forms of deformation, the length of the object does not change, but its straightness is out of tolerance.
241. Angular deformation: one of the basic forms of deformation, refers to the object parts and components of the angle between the composition of the change beyond the tolerance, called angular deformation.
242. Corrective part: the location of the steel structure deformation to impose corrective means, sometimes the corrective part is not necessarily the deformation of the parts.
243. Steel structure parts: a variety of parts through welding, riveting or bolting and other ways of connecting into one, these parts are interconnected and mutual restraint, forming an organic whole, usually called steel structure parts.
244. What are the causes of deformation of structural steel parts?
A: There are two reasons:
(1) Deformation caused by external forces.
(2) Deformation caused by internal stress.
245. The basic forms of welding deformation are longitudinal and transverse shrinkage deformation, bending deformation, twisting deformation, and angular deformation.
246. steel structure in the application of a thin steel plate, what are the characteristics?
A: The application of thin plates in steel structures is often assembled or welded together with various types of frames, subject to the limitations of the frame.
247. The extent of cross-sectional deformation of tubing during bending depends on the values of relative bending radius and relative wall thickness.
248. Tube bending, not the relative bending radius and the relative wall thickness of the larger value, then the greater the deformation.
249. If the curvature of the bent pipe is not enough, but similar, it can be taken on the outside of the pipe with water cooling, so that the inner metal shrinkage approach to increase the curvature, right?
A: No.
250. Currently, in the general field of bending, in the case of bending deformation section, ellipticity requirements are not too strict, and the use of coreless pipe bending often does not install anti-deformation devices, right?
A: No.
251. Pipe bender, according to the transmission mode, is divided into two kinds of mechanical transmission and gear transmission, right?
A: No.
252. There are two travel switches on a pipe bender to control the desired bend length by adjusting the position of the stopper.
253. The hydraulic tube bender is characterized by smooth transmission, reliable, low noise, compact structure, and can bend different billets, right?
A: No.
254. The method of bending or forming a billet by rotating a shaft is called roll bending.
255. The advantage of roll bending and forming is that the throughput is strong, plate roll bending generally needs to add other process devices to the rounding machine.
256. In order to take out the cylindrical workpiece after bending, the upper axis of the supporting part of the roll is movable at both ends, so you can take out the workpiece, right?
A: No.
257. In the rolling process, it should be commonly to sample to check that the curvature is best not rolled too small, right?
A: No.
258. Bending and forming are: press bending, broaching, bending, and hand bending.
259. In the bending process, by adjusting the upper and lower rolls, what can be bent into any curvature less than the curvature of the upper roll?
A: rely on adjusting the relative position of the upper and lower rollers, on the line.
260. Rounding machine: vertical and horizontal two categories.
261. There are three-axis and four-axis horizontal rounding machines, and what are the two types of three-axis?
A: Symmetric and asymmetric types.
262. Symmetric three-axis rounding machine, the three rollers of the roller core into what shape?
A: Isosceles triangle.
263. Material in the roll cylinder, adjust the distance between the shaft rollers must keep the center of the rollers is aligned with each other.
A: Be sure to keep the centers of the roll shafts parallel to each other, otherwise, the workpiece produces a taper.
264. When a pipe is bent, what force is applied to the material on the outside of the neutral layer to thin the pipe wall? What force is applied to the material on the inside to make the pipe wall thicker?
A: The role of tensile stresses is to make the wall thinner, the role of compressive stresses is to make the wall thicker.
265. When a pipe is bent, what is likely to happen when it is bent in a free state because the cross-section is circular and the stiffness is insufficient?
A: Easily flattened deformation.
266. The main processes of manual pipe bending are: sand loading, scribing, heating and bending.
267. When bending a seamed billet, where is the seam located as far as possible?
A: Center layer.
268. The bent portion of the bend must undergo: pressure test to check for leakage.
269. How do asymmetric three-axis rollers eliminate straight ends at the start?
A: Asymmetric three-axis rounding machine, rolling out the workpiece is only the beginning of the straight end. As long as the workpiece is inverted after the first roll over the head in the roll once, both ends of the straight end can be eliminated.
270. Anti-deformation method: that is, before the billet enters the bending deformation zone, a certain amount of deformation is applied in advance so that the outer wall of the pipe protrudes, to offset or reduce the deformation of the section in the bending.
271. In small batches or single-piece assembly of T-beams, generally taken: scribing assembly.
272. When assembling T-shaped and work-shaped sorghums, what assembly is generally used to increase assembly speed further?
A: Assembly using molds.
273. The longitudinal shrinkage of a weld decreases as the length of the weld increases, correct?
A: No.
274. The railing of a bridge crane is a truss structure with the same upper arch as the main girder.
275. Box girders, bridges, and frames are likewise required to have a certain amount of up-arch, the up-arch of their center section should be greater than the allowable deflection of the girder, correct?
A: No.
276. The prefabricated upper arch of the web of a box girder should be greater than that of the main girder because of the self-weight of the bridge and the effect of welding deflection.
277. When the steel plate is thin and the weld is in a position in the middle of the plate, then after welding, wave deformation often occurs.
278. Deformation of the weld body is caused when the weldment itself cannot overcome the shrinkage of the weld.
279. Methods of preventing and minimizing weld distortion include: the anti-deformation method, the correctly selected welding sequence, the rigid fixation method, and the hammering of the weld.
280. What is called a parallel line of this projection? What is the nature of the projection of that line?
A: When a straight line is parallel to the plane of projection, it is said to be parallel to the plane of projection. The projection of the line is true.
281. Any sheet metal has a thickness, and the thickness of the sheet has an effect on the shape and size of what drawing?
A: It affects the shape and size of an expanded drawing.
282. How are the surfaces of spheres, rings, and spirals developed?
A: The surfaces are non-developable.
283. What is the general method of unfolding prisms and cylinders?
A: Parallel lines are usually used.
284. What method is often used to find the line of coherence between a conical pipe and a cylindrical pipe that are orthogonal to each other?
A: The auxiliary plane method is often used.
285. The real length of a curve is often found by the method of expansion.
286. When a friction press is overloaded, it will only cause sliding between what and what without damaging the parts?
A: It causes sliding between the flywheel and the friction disk without damaging the parts.
287. The stroke of the slide of an open crank press can be adjusted by changing the eccentric bushing on the upper part of the connecting rod and the center distance of the spindle.
288. In the deep-drawing, extrusion process, what is the more stringent requirement for the material because of the die clearance?
A: Tighter requirements on the thickness tolerance of the material.
289. The separation process of sheet material during blanking can be broadly categorized into: elastic deformation, plastic deformation, and cracking separation.
290. What is the deep-drawing coefficient? The greater the degree of deformation of the material deep-drawing coefficient.
A: The smaller the coefficient of deep drawing, the greater the degree of deformation of the material during deep drawing.
291. Cold stamping: A stamping process performed at room temperature is known as cold stamping.
292. Composite process: The combination of two or more basic processes to be completed in one stroke of a press is called a composite process.
293. Simple blanking die: In one stroke of the press, it can only complete a blanking process of the die.
294. Composite blanking die: A blanking die that can perform several processes at the same time under one stroke of the press.
295. How to explain the blanking force correction factor Kp?
A: In the calculation of the blanking force, taking into account the wear of the die edge, die clearance, the mechanical properties of the material and other factors, and the selection of the safety factor, in general, take Kp is equal to 13.
296. Oblique edge blanking: A method to reduce the blanking force. It is to make the edge of the die inclined at a certain angle relative to the blank, so that the contact between the edge of the die and the blank during blanking is gradual, making the load uniform and smooth.
297. Stepped convex die blanking: A method of reducing the blanking force. When punching multiple holes at the same time, the punch is made in the form of a step with varying heights relative to the blank, which effectively distributes the punching force during punching.
298. What is the difference between an open crank press and a closed crank press?
A: Structurally, the bed of an open crank press is C-shaped, with a connecting rod transforming the rotary motion of the offset mandrel into the up-and-down reciprocating motion of the slide. The bed of a closed-type press has a frame-shaped structure, with a crank replacing the eccentric shaft.
299. What are the characteristics of an open crank press and a closed crank press?
A: The C-shaped bed of an open crank press is open on three sides and is particularly suitable for stamping the edges of large sheets. However, this form of bed structure is inherently less rigid and thus can withstand less load. The columns limit the frame structure of the closed crankshaft press, the table area is limited, and the operating space is small, thus, the peripheral dimensions of the stamped parts are somewhat limited. The rigidity of the bed of the frame-shaped structure is good, and the loads borne are large and uniform.
300. The factors affecting the stamping of materials are: elasticity, plasticity, hardness, quality of the surface condition of the material, and thickness tolerance of the material.
301. What is the effect of die clearance on the quality of punching?
A: When the clearance between the convex and concave dies is too small, the crack of the material near the edge of the convex die will be staggered outward for a certain distance, so that the part of the material in the middle of the upper and lower lines will be sheared for the second time with the punching, which affects the quality of the section. When the gap is too large, the crack of the material near the edge of the convex die is staggered inward for a certain distance, the material is greatly stretched, and the burr, collapse angle and slope of the material edge are larger, which will also affect the section quality of the punched part. In addition, too small or too large a gap has an effect on the dimensional deviation of punched parts.
302. What are the factors affecting the minimum bending radius of a material?
A:
(1) The mechanical properties and heat treatment state of the material
(2) The bending angle of the workpiece
(3) the geometry and size of the material
(4) the direction of bending
(5) other aspects, such as the thickness of the material, the quality of the surface and sides, and so on.
303. The neutral layer of the material in bending is: The material in the bending process, the outer layer is subjected to stretching, the inner layer is subjected to extrusion, there is bound to be a neither tensile nor compressive transition layer in its section, the stress is almost equal to zero, this transition layer is called the neutral layer of the material.
304. What should be fully considered in the correction of members consisting of multiple beams and columns in relation to each other?
A: To give full consideration to the linkage between beams and columns.
305. What must be ensured to comply with the requirements when correcting the deformation of thin plates in steel structures?
A: It must be ensured that all types of frames meet the requirements before correction of thin plates can be considered.
306. What is the relationship between the heating points of spot heating and the plate? What should be the distance between the heating points?
A: The heating point of spot heating is related to the thickness of the sheet. The distance between the heating points should be uniform.
307. Longitudinal shrinkage: A form of contraction of the weld and the metal near the weld, the contraction along the length of the weld is called longitudinal shrinkage.
308. Transverse shrinkage: A form of shrinkage of the weld and the metal near the weld, referring to the shrinkage perpendicular to the direction of the length of the weld, called transverse shrinkage.
309. How are the internal stresses generated in steel structural members?
A: The welding process is an uneven heating and cooling process for rivet-welded structures, which is the main cause of internal stresses in rivet-welded structural components. In addition, each part in the steel structure, in its billet state or processed into a part, may have residual stresses. After welding into a whole, these residual stresses may be assembled into a member of the new internal stresses.
310. Why is it necessary to carry out stress-relieving treatment for some steel structure parts after welding?
A: Some steel structure parts after welding, due to their good steel and no obvious welding deformation, but the welding stress is quite large, in the steel structure used for a period of time, may be released for some reason and cause deformation, so in damage. Therefore, for certain important uses of steel structures, such as high-pressure vessels, containers of hazardous media, boilers, etc., various methods of stress relieving treatment are used after welding with the aim of preventing the internal stresses in the steel structural members from causing harm to the members.
311. What are the factors affecting the welding deformation of steel structure parts?
A: design and process aspects. Design refers to the rationality of the structural design, the location of the weld, the form of welding bevel, etc.. Process refers to the reasonable welding process procedures, welding sequence, a variety of anti-deformation and anti-cracking methods used, as well as the adoption of stress relief measures.
312. How to understand the intrinsic connection of steel structure parts?
A: The so-called steel structure parts are a variety of parts through welding, riveting or and bolting and other ways to connect into one, these parts are linked to each other, and each other’s restrictions, forming an organic whole.
313. What is the key to correcting the deformation of a steel structure?
Answer:
(1) Analyze the cause of component deformation, to clarify the deformation is caused by external deformation, or deformation caused by internal stress
(2) Analyze the internal connection of the component, to clarify the constraints between the various components
(3) Choose the correct correction part, first solve the main contradiction, and then solve the secondary contradiction
(4) To understand and master the nature of the steel used in the component, in order to prevent the correction of the workpiece caused by breaking, cracking or rebound, etc.
(5) In accordance with the actual situation to determine the method of correction, and a variety of methods and the order of precedence.
314. What kind of correction method can only be used to correct the deformation of a thin plate in a steel structure?
A: For the deformation of a thin plate in a steel structure, only local heating (and spot heating) can be used for correction.
315. What should be paid attention to when spot heating is used to correct the deformation of thin plates?
A: Attention should be paid to:
(1) the heating temperature should be appropriate, not only to be able to cause enough plastic deformation of steel, the temperature can not be too high, generally 650 ℃ ~ 800 ℃.
(2) The size of the heating point and the distance between the point and the point should be appropriate. In general, depending on the thickness of the plate, the arrangement should be uniform, more plum-shaped layout.
(3) The purpose of pouring water to cool sharply and hammering with a wooden hammer is to accelerate the contraction of the fiber group of the steel plate.
(4) When heating the gas welding torch should not sway back and forth, the bundle of small flames should be perpendicular to the steel plate, and the heating point should not be too much, so as not to increase the undue internal stress.
316. What are the characteristics of the deformation of frame-type components?
A: frame components of more parts, in the structure of stronger mutual constraints, the deformation of each other has a great impact.
317. Simmering round machine bending blanks, usually after heating, right?
A: No.
318. When heating and bending, the material should be heated to 950 ℃ ~ 1100 ℃. At the same time, heating should be uniform, and the end temperature should be not less than 700 ℃.
319. Defects that may occur when bending cylinders are: defects that may occur when bending cylinders are crooked, unequal curvature, excessive curvature, center bulge and so on.
320. Roll bending cone, as long as the center of the upper shaft is adjusted to what position, while making the axis of the roll axis always coincide with the axis of the fan-shaped blanks, can be rolled into a cone?
A: Adjusted to an inclined position.
321. When rolling cones, which edge of the blank is increased in friction? So that the speed of what shift is lower than the speed of what shift?
A: Increase the friction of the small mouth of the blank, so that the speed at which the small mouth moves is lower than the speed at which the large mouth moves.
322. There are many forms of core bending shaft, there are rounded, pointed, hooked and what type?
A: and one-way joint type, universal type and so on.
323. Coreless pipe bending is not mandrel, in the bending machine, what process is used to control what deformation of the bending pipe bending method?
A: In the pipe bending machine using the process of reverse deformation is used to control the deformation of the pipe section bending method.
324. When the bending radius of the bend is greater than the diameter of how many times generally use coreless pipe bending?
A: greater than 1.5 times.
325. Extrusion bending is the use of metal plasticity, at room temperature, the billet is pressed into the mold to form a pipe elbow.
A: The billet is pressed into the mold with a curved shape to form a pipe elbow.
326. When extrusion bending, the billet is subjected to bending force moments in addition to the action of the bending force, but also subjected to axial and frictional forces in the opposite direction of the axial force.
327. Briefly describe the process of bending blanks in the rounding machine.
A: In bending, the blank is placed between the upper and lower rollers of the rounding machine, due to the rotation of the rollers, and through the friction between the upper and lower rollers and blanks, the blanks are moved, thus continuously forming a bend.
328. The advantage of the four-axis rounding machine is that it enables both ends of the sheet to be rolled, thus eliminating the straight ends, simplifying the process, reducing the workload and improving the production efficiency over the three-axis rounding machine.
329. The methods of rolling cones are: zonal rolling method, rectangular feeding method, rotary feeding method, small mouth deceleration method and so on.
330. How can the ellipticity of the cross-section be reduced when bending tubes?
A: In order to minimize the ellipticity of the cross-section when bending tubing, it is often used in the production process to bend the tube by adding filler inside the tube, or by using a roller with a conical groove to press on the outside of the tube, or by using a mandrel to penetrate the inside of the tube.
331. What are the advantages of a spoon mandrel?
A: The Spoon mandrel and the outer wall of the supporting surface are large, anti-flattening effect is better than the tip type. The surface is not easy to wrinkle in the pipe bending, and spoon mandrel manufacturing is also more convenient, so it is more widely used.
332. What are the advantages of coreless pipe bending over core bending?
A: (1) To reduce the bending of a large number of pre-prepared cores and other work, thereby improving productivity.
(2) To avoid the manufacture of mandrels, reducing costs.
(3) The tube does not require lubrication, saving the lubricant and oil spraying process.
(4) Ensure the quality of the bent pipe.
(5) There is no mandrel and pipe wall friction, reducing the torque when bending, thus extending the service life of the pipe bender.
333. Mechanical drive type pipe bender is how the transmission?
A: By the motor through the gear shaft, deceleration mechanism, worm gear transmission, drive the bending die rotation.
334. When assembling the ring seams of the connected cylinders on the roller frame, the lateral distance and height position of each pair of rollers should not be the same, so that when assembled, the cylinders can be concentric, right?
A: No.
335. Suppose there is a deviation in the diameter of two cylinder sections. In that case, the cylinder section with the larger diameter should be padded during assembly to obtain concentricity between the two sections, correct?
A: No.
336. The greater the coefficient of linear expansion of the weldment material, the greater the post-weld shrinkage.
337. Carbon steel shrinks more after welding than stainless steel and aluminum, correct?
A: No.
338. When preventing distortion of a multilayer weld by the hammer weld method, hammering should be applied to the first and last layers, correct?
A: No.
339. The use of the rigid fastening method causes great internal stresses in the weld area, making this method suitable for medium carbon and alloy steels, correct?
A: No.
340. What is often used to assemble longitudinal seams in cylinders to improve assembly efficiency?
A: Levers and screw tensioners are often used to improve efficiency.
341. What is often used to adjust the ellipticity that occurs in thin-walled cylinders?
A: Radial push-ups.
342. What can be used to ensure that the whole of the long, thin cylindrical joints do not bend when they are butted together?
A: Rollers are used for assembly to ensure that no bending occurs.
343. What is utilized to clamp and align the ring seams of vertically butted cylinders to achieve better results while still obtaining the required clearance?
A: The use of wedge clamps to clamp and align the ring seams will give better results and also give the required clearance.
344. What is used to locate the ring seam of a cylinder with a lap in the vertical installation? What is used for final clamping?
A: Positioning with a retaining iron. It is finally clamped with a round verge-shaped wedge.
345. A rivet gun consists of a handle, a body, a trigger, and a tube fitting.
346. Before cold riveting, in order to eliminate hardening to improve the plasticity of the material, rivets must undergo: annealing treatment.
347. What does a blind rivet consist of, and what is it made of?
A: It is composed of a hollow rivet and a mandrel.
348. When a weld cools, what is produced in the weld area? And what force is produced within the weld?
A: When the weld cools, contraction occurs in the weld area, resulting in internal stresses within the weld.
349. In a multilayer weld, the first layer causes the greatest shrinkage, and the second layer shrinks approximately what percent of the shrinkage of the first layer? What percent of the shrinkage of the second layer is approximately that of the first layer?
Answer: (1) Twenty percent (2) Five to ten percent.
350. The arch over the main girder of a bridge crane is normally one thousandth.
351. A bridge crane consists of (bridge, an operating mechanism, load carriage.)
352. The main girder of a box-row structure consists of: upper cover plate, lower cover plate, web, long and short reinforcement plates.
353. What is the maximum permissible peak value of the web face of a main beam of a box-row structure over a length of one meter for the compression zone? What is the maximum permissible wave peak in one meter of length for the compression zone and the tension zone?
A: 0.7t for compression zone, 1.2t for tension zone.
354. How much allowance is required for undercutting the web of a box girder? How much of the center can not have joints?
A: A margin of 1.5/1000 is required, there should be no joint at two meters from the center.
355. There are various types and shapes of steel roof racking according to the use and need. Generally, there are: triangular, trapezoidal, spherical, mesh roof racking, etc.
356. The height of a triangular roof frame is generally 1/4 to 1/5 of the span.
357. Steel roof frames are mostly assembled using profiling.
358. Cold riveting: Riveting at room temperature is called cold riveting.
359. Pull riveting: Pull riveting is another riveting method of cold riveting. It uses manual or compressed air as a power source, through a special tool to make the rivet and the riveted parts riveted together.
360. Hot Riveting: Riveting with heated rivets is called hot riveting.
361. Anti-deformation method: analyze the direction and size of the weldment may produce deformation after welding, before welding should make the welded parts to do the same size, the direction of the opposite deformation, in order to offset or compensate for the deformation that occurs after welding, so as to achieve the purpose of preventing the deformation of the weldment, this method is known as anti-deformation law.
362. Rigid fixing method: the use of assembly fixtures or temporary support, the mutual position of the weldment will be fixed to prevent post-weld deformation of This method is called the rigid fixing method.
363. The layout drawing is based on the construction drawings drawn from the drawings, right?
A: No.
364. In addition to flat surfaces, there are also cylindrical and conical surfaces.
365. All lines on a spread drawing are solid lengths of the corresponding portion of the member’s surface.
366. If a line segment is cumulative in one of the three projections, then the other two projections must be real, i.e., respond to the real length of the segment, correct?
A: No.
367. If two projections of a line segment are perpendicular to the axis of projection in which they are interposed, then the third projection must reflect the real length of the segment, correct?
A: No.
368. The projection of a straight line is always a straight line, and there is no other case, correct?
A: No.
369. A line in general position sometimes responds to real length and sometimes does not respond to real length in three views.
370. For the real length of a line in general position, it is better to find it by rotation, right?
A: No.
371. The methods for finding the real length of a line segment are the parallel line method, the triangle method, and the radial line method, correct?
A: No.
372. The right triangle method, the rotation method, the transposed plane method, and the branch line method are commonly used in the production of riveters or sheet metal workers.
373. When unfolding a form by the triangle method, the key is to find the real length of each polyline, correct?
A: No.
374. Plane curves respond to real lengths in all three views, correct?
A: No.
375. Prisms, cylinders, cylindrical surfaces, etc., can be expanded by the parallel line method.
376. The trigonometric method of unfolding applies to the unfolding of forms in which the plane lines of the surfaces of all members intersect at one point, correct?
A: No.
377. When solving for a coherent line by the auxiliary surface method, the axes of a rotary body must be parallel and respond to a real length, correct?
A: No.
378. The presses commonly used by riveters are: hydraulic presses and air presses.
379. How does the final riveting temperature affect the riveted joint?
A: Too high and the initial stress in the shank will be reduced, too low and the rivet will become blue brittle.
380. What is the function of the shank of a drill?
A: To clamp and transmit the torque and axial force required for drilling.
381. The hammers commonly used by riveters are: hand hammers, sledge hammers, and type hammers.
382. The two main types of chisels commonly used by riveters are flat chisels and narrow chisels.
383. Iron-carbon alloys containing less than 2.11% carbon are called steels.
384. Steels containing more than 0.6% carbon are called high-carbon steels.
385. Steel is classified according to its use: structural steel, tool steel and special-purpose steel.
386. Steel can be divided according to its end shape: plate, pipe, profile, wire.
387. Steel deformation correction of the basic methods is: cold work correction and heating correction.
388. Assembly fixture: refers to the assembly process used to apply external forces on the part, so that it is reliably positioned process equipment.
389. The basic methods of cold straightening are: manual straightening and mechanical straightening.
390. Heating correction: full heating correction and local heating correction.
391. local heating correction heating zone shape: point, line, triangular, three.
392. Angle steel deformation: twisted, bent, and angular deformation of three kinds.
393. The deformation of channel steel includes twist, bend, and wing plate local deformation.
394. Cold work correction: Correction at room temperature is called cold work correction.
395. Separation consists of three processes: drop, punch, and notch.
396. Stamping: The process of separating or shaping a sheet to obtain a manufactured part.
397. What are the advantages of stamping?
A: Good product quality, high productivity, material savings, cost reduction, and easy to automate.
398. Bending molding: bending the blank into the desired shape of the processing method.
399. The basic forms of riveted joints are: butt joint, lap joint, and corner joint.
400. Riveted joint: the use of rivets to join two or more members into a single unit.
401. Commonly used rivets are: semi-circular head, countersunk head, semi-countersunk head, flat head, flat taper head, flat round, flat.
402. Types of rivets are: strong riveting, dense riveting tight riveting.
403. Assembly: the combination of parts into components in accordance with certain technical conditions.
404. The three elements of assembly are: positioning, support and clamping.
405. Metal structure connection methods are: welding, riveting, bolting, and hybrid welding connections.
406. The tools commonly used for sample proofing are: chalk line, stone pen, drawing pin, ruler, sample punch, and hand hammer.
407. The main methods for the coherent line are: plain line method, auxiliary plane method, and spherical method.
408. Methods of finding the real length of a straight line segment include: rotation, right triangle method, transposition, and branching.
409. Methods of making unfolding diagrams include: the graphing method and the calculation method.
410. Commonly used methods of unfolding include: the parallel line method, the radial line method, and the triangle method.
411. Material shear section can be divided into: collapsed angle, bright band, shear band, burr.
412. Correction points: manual correction, mechanical correction, flame correction.
413. Benchmark: parts drawing used to determine the location of other points, lines, cotton points line surface.
414. Plasticity: metal materials under the action of external forces, permanent deformation without destroying the ability.
415. Toughness: the ability of metal materials under the action of impact loads not to be destroyed.
416. Prevention of welding deformation is: anti-deformation method, rigid fixation method, and reasonable welding sequence.
417. Spatial rectilinear projection has realism, accumulation, and contraction.
418. Intersecting lines: intersecting lines produced by cutting a form in a plane.
419. Coherent line: by two planes intersecting, two produced by the surface of the intersection line.
420. Viewpoints: basic view, partial view, oblique view, rotational view.
421. Basic views are: principal, top, left, right, elevation, rear.
422. Section views: full, half, partial.
423. How does cutting volume affect drilling?
A: Proper selection of cutting volume prevents premature wear or damage to the drill. Prevent overloading of the machine tool, improve the cutting accuracy and surface roughness of the workpiece.
424. Tapping: Use a tap to cut internal threads on the hole wall.
425. What effect does the size of the bottom hole diameter have on the work of the tap?
A: If the diameter of the bottom hole and the diameter of the internal thread of the same material expansion are the same, then the tap is easy to break, if too large, it will make the tapping of the thread tooth height insufficient to form scrap.
426. Sleeving: Use plate teeth to cut threads in the outer diameter of round rod pipe.
427. When selecting of bevel, should we pay attention to what principles?
A: (1) minimize the amount of weld metal filler
(2) Ensure weld penetration and avoid cracks
(3) Consider the minimum welding deformation
(4) Easy processing.
428. Leave a blunt edge when beveling can be: to prevent burn-through joints.
429. Beveling methods include: wind shovel processing, machining, gas cutting beveling, and carbon arc gas planing beveling.
430. Carbon arc air planing: the use of a carbon electrode arc of high temperature to the local melting of the metal, and then using compressed air flow to blow off the molten metal, to achieve the purpose of planing or cutting metal.
431. Grinding: Elimination of burrs on the edges of weld scars on plate surfaces, grinding of welds and grinding of welds on pressurized vessels prior to re-testing and inspection.
432. Bending molding: the flat blank, profile or tube, bent into a certain angle, curvature, so as to form a certain shape of the part.
433. Elastic recovery phenomenon: elastic deformation of the material when bending, when the external force is removed, part of the elastic deformation restores the original state, so that the shape and angle of the bent parts change.
434. The riveters commonly used methods of bending and molding are: compression bending, roll bending, calendering and water and fire bending plate.
435. Factors affecting the bending of molding are: bending force, elastic restoration phenomenon, minimum bending radius, and section shape.
436. According to the mechanical properties of the material to be bent, the bending mode and nature, the shape of the bending parts determines the size of the bending force.
437. Factors affecting bending resilience are: mechanical properties of the material to be bent, relative bending radius of the material, bending angle and some other factors.
438. What are the factors affecting the minimum bending radius?
A: The mechanical properties of the material being bent, the bending angle, the direction of bending of the material, the surface quality of the material and the quality of the shear section, and other factors.
439. Factors affecting the change in cross-section shape during bending are: relative bending radius, cross-section geometric characteristics and bending mode.
440. How does steel heating affect steel bending?
A: After heating, the steel bending force required to reduce the phenomenon of elasticity disappears, and the minimum bending radius decreases, which is conducive to controlling the deformation according to the processing requirements.
441. Heating is usually used for room temperature bending.
442. Why should the steel heating temperature be limited to a certain temperature?
A: Too high a temperature can easily cause steel overcooking, too low a temperature will make molding difficult, and cause cold hardening.
443. Using contact bending, what measures are often used to solve the problem of elastic recovery?
A: Correct the shape of the mold, use the pressure correction method, increase the crimping device, and reduce the mold clearance.
444. Compression bending: the use of a bending die in the press for the bending molding processing method.
445. Material bending deformations are: free bending, contact bending, and corrective bending.
446. Why do riveters use pressure molds, usually welded structures?
A: Because this is not only easy to manufacture, but can shorten the cycle of mold making, and also improve the utilization of materials, and reduce costs.
447. Roll bending: a bending molding processing method on a rolling bed.
448. A symmetrical three-roller plate rolling machine is often used (the two ends of the pre-bending and leave the processing allowance) to eliminate the straight edge of the workpiece.
449. What are the two types of calendering? What kind is commonly used by riveters?
A: No, thinning calendering and thinning calendering. The riveters often use the non-thinning calendering.
450. Rolling taper should be used to: adjust the position of the upper roller, so that it is inclined at an angle to the lower roller, so that the feed rate of the small mouth is greater than that of the large mouth.