In modern manufacturing, innovation cycles are becoming shorter, and companies need to respond quickly to customer demands. However, committing to mass production is not always the best choice, especially when a product is still in its testing or early launch phase. This is where low-volume manufacturing proves invaluable.
By producing anywhere from 50 to several thousand parts, businesses can bring products to market faster, reduce risks, and gain the flexibility to adjust designs along the way.
Table of Contents
1. What Is Low Volume Manufacturing?
Low volume manufacturing (LVM) refers to the production of parts in relatively small quantities compared to traditional high-volume manufacturing. Instead of investing in costly large-scale tooling and setting up long production runs, companies can use low-volume manufacturing to:
• Validate product designs before full-scale production.
• Produce small batches for market testing.
• Supply customized parts for niche applications.
• Bridge the gap between prototype and mass production.
This approach is especially beneficial for industries where precision, flexibility, and responsiveness are critical.
2. Core Processes in Low Volume Manufacturing
Low volume manufacturing is not tied to a single process—several complementary technologies support it. Each method offers unique advantages depending on the material, complexity, and quantity required.
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a versatile solution for small-batch production, offering:
• High dimensional accuracy and repeatability
• Wide material selection, including metals (aluminum, steel, titanium) and plastics.
• Superior surface finishes suitable for functional prototypes and end-use parts.
Because no hard tooling is required, design changes can be easily implemented between runs.

3D Printing
3D printing is ideal for rapid iterations and highly complex geometries that traditional methods cannot easily achieve. Benefits include:
• No need for molds or tooling.
• Fast turnaround times.
• Support for lightweight structures and intricate designs.
This makes it a popular choice in industries like aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
Injection Molding (Low-Volume Tooling)
For plastic parts that need production-like quality, low-volume injection molding provides a reliable option:
• Use of aluminum or soft steel molds reduces lead time and tooling cost.
• Consistent quality across hundreds or thousands of units.
• Suitable for bridge production and market testing before mass scale-up.
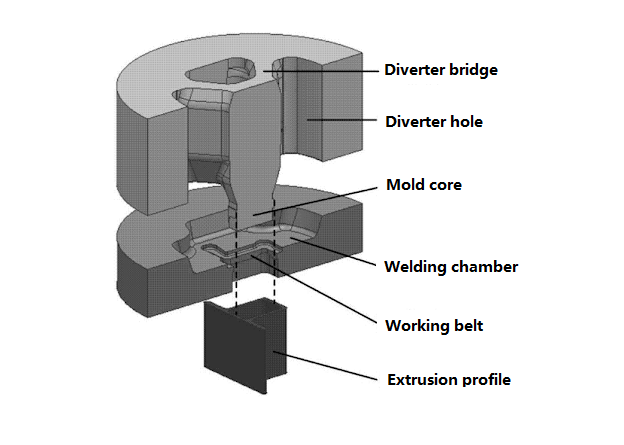
Extrusion
Extrusion is a process that forces material through a die to create objects with a fixed cross-section, suitable for low-volume production of custom profiles. Benefits include:
• Efficient production of continuous shapes like rods, tubes, and channels.
• Wide material compatibility, including aluminum, plastics, and composites.
• Ideal for producing small batches of specialized lengths or profiles.
Low-volume extrusion allows for design adjustments without large-scale tooling changes, making it flexible for prototyping and niche applications.
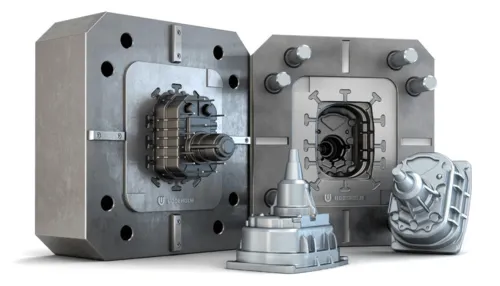
Die Casting
Die casting can be adapted for low-volume metal parts, providing precision and durability. Key advantages include:
• Ability to produce complex shapes with tight tolerances.
• High-quality surface finishes suitable for functional parts.
• Reduced setup costs for small production runs compared to full-scale mass production.
Low-volume die casting is ideal for limited-run components that require consistent strength and dimensional accuracy.
Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting uses a silicone mold to replicate a master part under vacuum conditions, suitable for short-run production. Benefits include:
• Produces high-fidelity parts from plastics or resins.
• Cost-effective method for small batch production.
• Excellent for functional testing and bridge production before mass manufacturing.
Vacuum casting allows manufacturers to produce multiple units with consistent quality and appearance quickly.
Laser Cutting and Engraving
Laser cutting and engraving use high-powered lasers to precisely cut or mark materials such as metals, plastics, and composites. Advantages include:
• Ability to produce intricate shapes and detailed designs.
• Minimal material waste and high repeatability.
• Suitable for small batches, prototyping, or custom parts with complex patterns.
Low-volume laser processes allow fast design iterations without the need for expensive tooling.

4. Advantages of Low Volume Manufacturing
The real value of low volume manufacturing lies in its ability to balance speed, cost, and flexibility.
Faster Time-to-Market
Companies can respond quickly to customer demand and launch products without waiting months for full production.
Cost-Effective Production
Lower tooling and setup costs compared to high-volume manufacturing make it ideal for startups or small-scale projects.
Design Flexibility & Iteration
Adjustments can be made between batches, helping refine designs and improve performance based on real-world feedback.
Risk Reduction
Instead of committing to thousands of parts, businesses can test smaller runs and minimize financial risk.
Support for Customization
Perfect for industries where products need to be tailored—medical devices, aerospace components, and consumer electronics often require customized small batches.
5. Applications of Low Volume Manufacturing
Low volume manufacturing plays a critical role across multiple industries:
- Aerospace & Defense – Small-batch precision components for testing and specialized systems.
- Medical Industry – Customized surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic device parts.
- Automotive – Bridge production for new models, aftermarket parts, and concept car components.
- Consumer Electronics – Short runs for new device launches, testing new designs with real users.
- Industrial Equipment – Replacement parts and niche tools for specialized applications.
6. Low Volume Manufacturing vs. Prototyping vs. Mass Production
| Feature | Prototyping | Low Volume Manufacturing | Mass Production |
| Quantity | 1–50 units | 50–5,000 units | 5,000+ units |
| Purpose | Testing & validation | Market testing / bridge production | Full-scale supply |
| Lead Time | Fast | Moderate | Longer setup |
| Cost | Low (per unit high) | Balanced | Low (per unit) but high tooling |
| Flexibility | Very high | High | Limited |
This makes low volume manufacturing the ideal bridge between early prototyping and large-scale mass production.
7. Conclusion
Low volume manufacturing offers companies the speed, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness needed to stay competitive in today’s fast-moving markets. Whether you are launching a new product, testing market demand, or producing specialized components, low volume manufacturing provides a smart pathway between prototype and mass production.
At YP-MFG, we provide end-to-end low volume manufacturing solutions, including CNC machining, 3D printing, injection molding, and sheet metal fabrication. Our team ensures high-quality parts, quick turnaround times, and tailored support for your unique project needs.
Contact us today to discuss your low volume manufacturing requirements and get a free project consultation.

YPMFG’s Low Manufacturing Service
We provide exceptional low-volume manufacturing and service to customers all over the world. Please let us know if you have any requests for items, technical issues or requests, and if you have any questions or concerns, please contact us at any time.




